
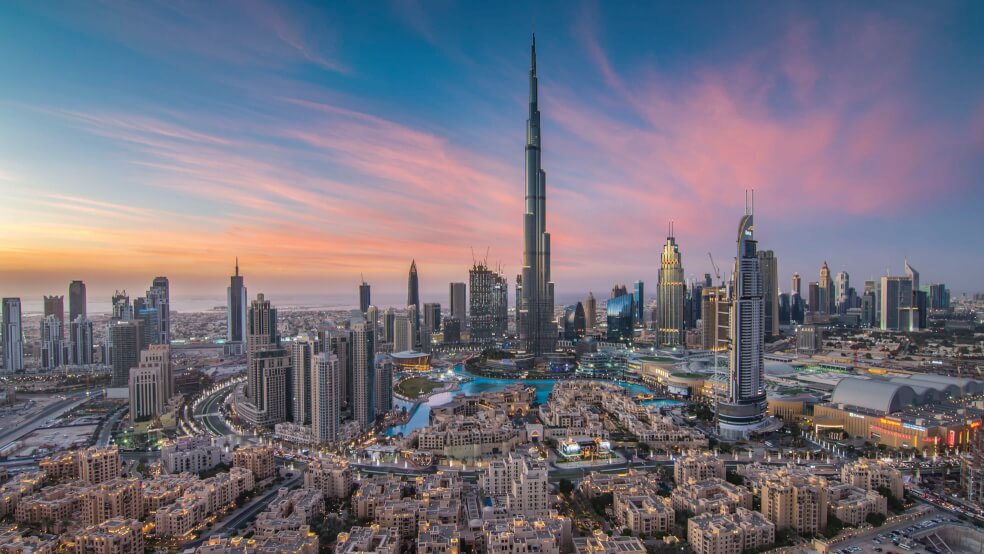
If you are thinking that Dubai country is a country then you would be wrong. Dubai is a city and it’s also a state (or Emirate), one of seven emirates that make up the United Arab Emirates (UAE), a country located in the Middle East. The UAE has seven emirates, namely: Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm Al Quwain, Fujairah and Ras Al Khaimah. Here is a table outlining their key characteristics:

| Emirate | Description | Key Features | Population (2022) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abu Dhabi | The largest and richest emirate, home to the capital city of Abu Dhabi. | Oil-rich, with a modern skyline and many cultural attractions. | 2,784,490 |
| Dubai | The most populous and popular emirate, known for its skyscrapers, shopping malls, and artificial islands. | Tourism and trade hub, with a rapidly growing economy. | 4,177,059 |
| Sharjah | The third most populous emirate, known for its Islamic heritage and cultural attractions. | Home to many mosques and museums, as well as the Sharjah International Film Festival. | 1,469,090 |
| Ajman | The smallest emirate, with a quiet and relaxed atmosphere. | Popular with tourists for its beaches and water sports. | 504,846 |
| Umm Al Quwain | The second smallest emirate, with a traditional Arabian feel. | Home to the Umm Al Quwain Museum and the Al-Nakheel Fort. | 72,000 |
| Ras Al Khaimah | The northernmost emirate, with a mountainous landscape and beautiful beaches. | Popular with tourists for its outdoor activities and adventure sports. | 416,600 |
| Fujairah | The southernmost emirate, with a coastline on the Gulf of Oman. | Home to the Fujairah Fort and the Fujairah National Museum. | 152,000 |
As mentioned Dubai is not just a city, but also an Emirate. Now most of the population of the Emirate of Dubai resides in the city of Dubai but there is more. The most populated area outside of Dubai City is Hatta, which is a mountainous area bordering with country of Oman. One day we will write an article about Hatta. It is a fascinating place, but for now, let’s talk about the city of Dubai.
Introduction
Dubai, often referred to as the “City of Gold,” is a fascinating blend of tradition and modernity, nestled in the heart of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). This glittering gem in the Middle East has rapidly transformed from a modest trading port to a global metropolis known for its breathtaking architecture, luxury shopping, and vibrant culture. In this article, we will embark on a journey through Dubai’s history, geography, governance, economy, attractions, Emirati culture, and essential guidelines for living in or visiting this remarkable city.
Table of Contents
Emirati Culture and Traditions
History of Dubai
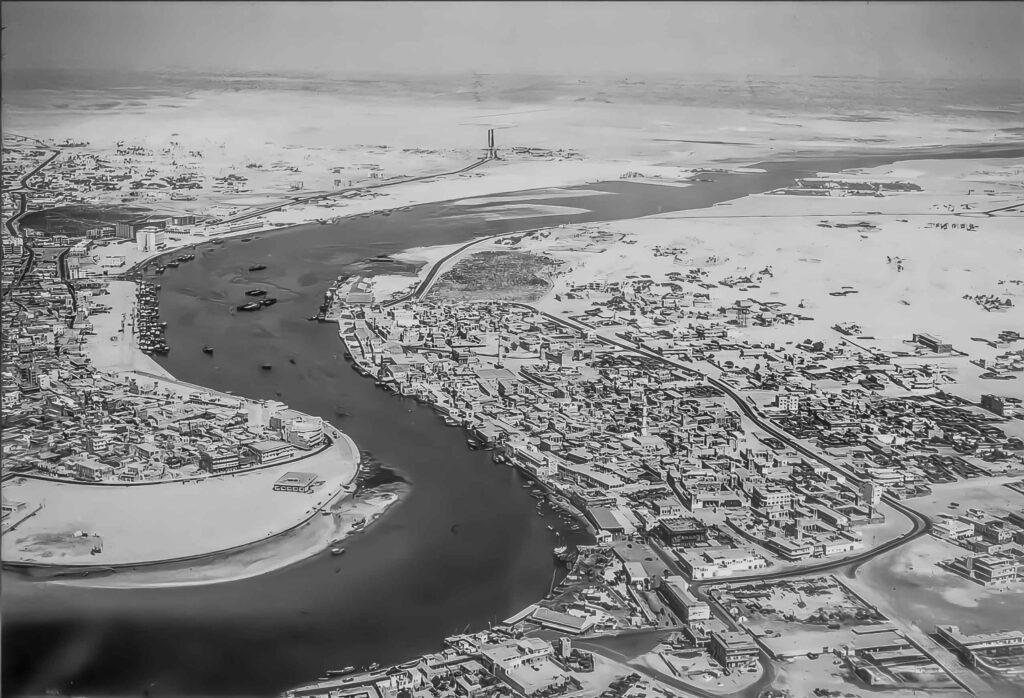
Dubai’s history is a tale of transformation and resilience, stretching back centuries. What we know today as a global economic hub was once a small fishing village situated along the shores of the Arabian Gulf. Dubai Country feels like a separate country but it is an Emirate. Here are some key milestones in Dubai’s historical journey:

Early Settlements
Dubai’s history as a settlement can be traced back to the 18th century when it was a small trading and fishing village inhabited by the Bani Yas tribe, led by the Al Maktoum family. Its strategic location along the ancient trade routes made it a natural trading post.
Pearl Diving Era
During the 19th century, Dubai’s economy thrived on pearl diving. The city’s inhabitants were skilled divers, and pearls were a valuable commodity that brought prosperity to the region. However, this era faced challenges, including the depletion of pearl oyster beds and the introduction of cultured pearls, which led to a decline in the industry.
British Influence
In the early 20th century, Dubai, like other emirates in the region, became a British protectorate. This influence helped establish law and order and introduced Dubai to modern infrastructure and governance practices.
Sheikh Saeed Al Maktoum’s Reign
One pivotal figure in Dubai’s history is Sheikh Saeed Al Maktoum, who ruled from 1912 to 1958. His leadership brought stability and growth to the emirate. He implemented economic diversification efforts, such as encouraging trade with neighbouring countries and expanding the Dubai country port facilities.
Formation of the UAE
Dubai played a significant role in the formation of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) in 1971. Along with six other emirates, Dubai joined the federation, marking the beginning of a unified nation. The visionary leadership of Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan and Sheikh Rashid bin Saeed Al Maktoum paved the way for the UAE’s development as a modern nation.
Economic Transformation
Dubai’s modern transformation began in the late 20th century. The discovery of oil reserves in the region provided a substantial economic boost, which was wisely invested in infrastructure and development projects. The establishment of free trade zones, such as Jebel Ali Free Zone, attracted foreign investment and international businesses.
Burj Al Arab and the Burj Khalifa
In the 21st century, Dubai made headlines with iconic architectural marvels. The Burj Al Arab, a luxury hotel shaped like a sail, and the Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest skyscraper, became global symbols of Dubai’s ambition and innovation.
Today, Dubai stands as a testament to its rich history and relentless pursuit of progress. It has evolved into a global business hub, a magnet for tourists, and a city that seamlessly blends tradition with modernity. The stories of its past are preserved in historic districts like Al Fahidi, where visitors can explore museums and heritage sites, gaining a deeper appreciation for Dubai’s remarkable journey through time.
Geography and Climate
Dubai’s geography is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes that contribute to its unique character and appeal.
Location and Topography
Dubai country is located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, along the shores of the Arabian Gulf. Its strategic position has historically made it a hub for trade and commerce. The city is surrounded by the emirate of Sharjah to the northeast and Abu Dhabi to the south.
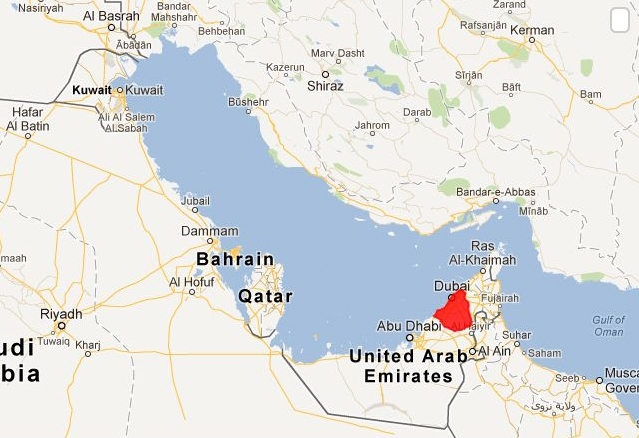
One of the most striking geographical features of Dubai is its contrast between the coastline and the desert. To the east, the city meets the Arabian Gulf with a stunning coastline that stretches for approximately 72 kilometres (45 miles). The azure waters of the Gulf provide opportunities for water sports, leisure, and beautiful beachfront experiences.
Desert Landscape
Moving inland from the coast, Dubai’s landscape transitions into the vast expanse of the Arabian Desert. The desert plays a significant role in the emirate’s geography and history. Visitors can explore the mesmerizing sand dunes that extend beyond the city limits, offering a taste of the Arabian Desert’s natural beauty.
Hajar Mountains
To the northeast of Dubai country lies the Hajar Mountains, a rugged and arid mountain range that serves as a natural border with Oman. These mountains add a touch of geological diversity to the region, offering opportunities for hiking and adventure activities.
Climate
Dubai’s climate is characterized by its arid desert conditions, with high temperatures and minimal rainfall throughout the year. The city experiences a subtropical desert climate, which can be divided into two main seasons:
- Summer (May to September): Summers in Dubai country are hot and humid, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F). The heat is especially intense during July and August, making outdoor activities less comfortable. Visitors are advised to stay hydrated and seek air-conditioned spaces during this season.
- Winter (October to April): The winter months bring relief from the scorching heat, with daytime temperatures ranging from 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F). This is the ideal time for tourists to explore outdoor attractions and engage in activities like desert safaris.
Artificial Islands
Dubai’s innovative spirit is also reflected in its geography through the creation of artificial islands. The most famous of these is the Palm Jumeirah, an impressive man-made archipelago in the shape of a palm tree. It is home to luxurious resorts, villas, and an array of leisure facilities.
Dubai country’s geography, with its juxtaposition of desert, coastline, and man-made wonders, contributes to the city’s multifaceted charm. Whether you seek relaxation on pristine beaches, adventure in the desert dunes, or the allure of iconic skyscrapers, Dubai’s geography offers something for every traveller to marvel at and explore.
Governance and Leadership
Dubai is governed through a well-defined structure that combines traditional and modern governance practices. The governing structure of Dubai can be explained as follows:
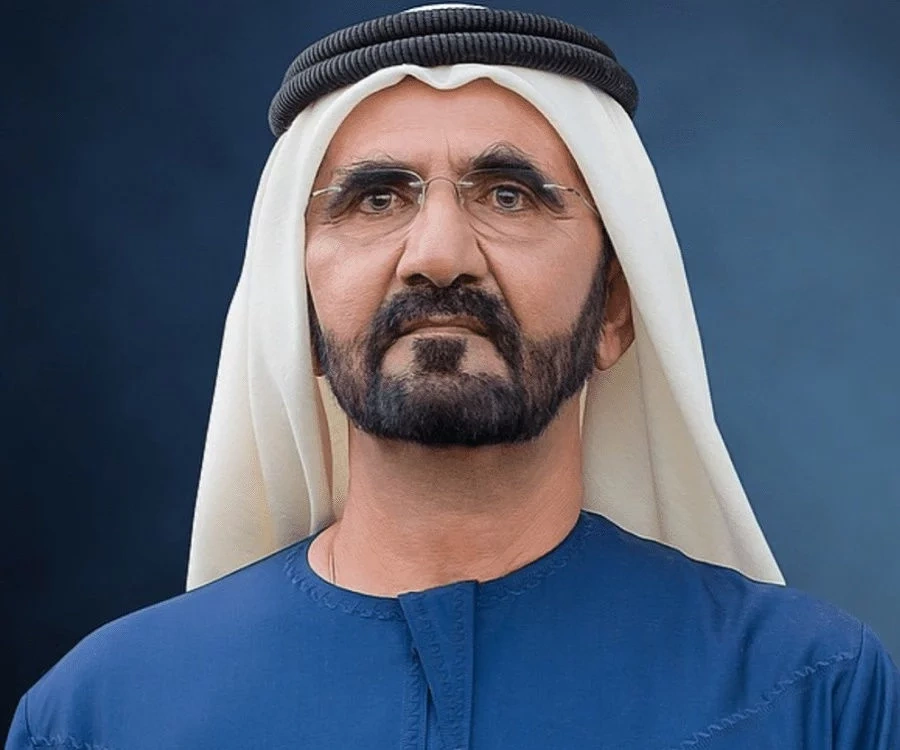

- Ruler of Dubai Country: At the top of the governance hierarchy is the Ruler of Dubai, who is also the Vice President and Prime Minister of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Currently, the Ruler of Dubai is His Highness Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum. The Ruler holds a central role in shaping Dubai’s policies and direction.
- Executive Council: The Dubai Executive Council is a key advisory and administrative body. It assists the Ruler in implementing policies and strategies for the emirate. The council is composed of high-ranking officials and experts from various sectors and plays a vital role in decision-making and policy formulation.
- Government Departments and Entities: Dubai’s government is organized into various departments and entities, each responsible for specific aspects of governance. These include the Dubai Municipality (responsible for urban planning and development), Dubai Police (ensuring law and order), Dubai Health Authority (overseeing healthcare services), Dubai Tourism (promoting tourism), and many others. These entities collectively contribute to the day-to-day administration and services provided to residents and visitors.
- Judiciary: Dubai has a separate judicial system that operates independently. The Dubai Courts oversee civil, criminal, and commercial cases. Dubai’s legal system is based on a mix of Islamic law (Sharia) and civil law principles, with a strong emphasis on fairness and transparency.
- Economic Development: Dubai has established various free trade zones, such as the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and Jebel Ali Free Zone, to attract international businesses. These zones offer incentives, tax benefits, and streamlined processes for companies operating within them, contributing to Dubai’s economic growth.
- Local Councils: Dubai is divided into several administrative areas, and each area has its local council responsible for addressing the needs and concerns of residents in that specific locality. These councils play a role in community development and representation.
- Leadership Succession: Dubai Country has a clear system of leadership succession within the ruling Al Maktoum family, ensuring stability and continuity in governance. The Crown Prince of Dubai, as designated by the Ruler, plays a significant role in supporting and assisting in the leadership of the emirate. The crown prince of Dubai is His Highness Sheikh Hamdan bin Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum.
Dubai’s governance structure is characterized by a balance between traditional leadership, which respects the emirate’s heritage and values, and modern governance practices, which promote economic development, innovation, and international engagement. This balanced approach has been instrumental in Dubai’s transformation into a global city and a centre for business, tourism, and culture in the Middle East.
Dubai’s Thriving Economy
The economy of Dubai is made up of many components, which are outlined below in this table:
| Sector | Contribution to GDP (2022) |
|---|---|
| Tourism | 20% |
| Trade | 18% |
| Real estate | 15% |
| Transportation and logistics | 12% |
| Financial services | 10% |
| Manufacturing | 9% |
| Construction | 6% |
| Other | 10% |
Dubai’s economy is characterized by several key sectors and strategies that have contributed to its prosperity and global significance.
1. Trade and Commerce
Historical Trading Hub: Dubai’s strategic location along ancient trade routes has long made it a center for trade and commerce. Its historical role as a hub for the import and re-export of goods contributed to its early economic development.
Modern Trading Hub: Today, Dubai remains a major global trading hub. The emirate boasts one of the world’s busiest ports, Jebel Ali Port, and a well-established logistics and transportation infrastructure. Dubai’s geographic location and excellent connectivity via air, sea, and land routes make it an ideal gateway for businesses looking to access markets in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia.
2. Tourism and Hospitality
Tourism Boom: Dubai’s tourism industry has experienced exponential growth. The city’s iconic landmarks, luxury resorts, shopping festivals, and cultural events attract millions of visitors annually. Dubai has positioned itself as a global tourist destination, offering a diverse range of attractions, from the Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest skyscraper, to the Palm Jumeirah, a man-made island with luxurious resorts.
Dubai Expo 2020: The hosting of the Dubai Expo in 2021 further boosted the tourism sector, showcasing innovation, sustainability, and cultural exchange on a global scale.
3. Real Estate and Construction
Skyscrapers and Mega-Projects: Dubai’s skyline is synonymous with impressive skyscrapers, including the Burj Khalifa and the Burj Al Arab. The emirate is also known for its ambitious construction projects, such as the Dubai Mall and various man-made islands. These projects not only redefine the cityscape but also drive economic growth.
Real Estate Investment: Dubai’s real estate market attracts both local and international investors. The emirate has established various freehold and leasehold property zones, allowing foreigners to own property in designated areas, which has further stimulated the real estate market.
4. Financial Services
Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC): DIFC is a financial free zone that serves as a regional and global financial hub. It hosts a wide range of financial institutions, including banks, investment firms, and insurance companies.
Islamic Finance: Dubai is a leading center for Islamic finance, offering a range of Sharia-compliant financial products and services.
5. Economic Diversification
Dubai Plan 2021: To reduce reliance on oil revenue and ensure a sustainable future, Dubai has implemented the Dubai Plan 2021. This strategic framework focuses on diversifying the economy into sectors such as technology, healthcare, renewable energy, and advanced manufacturing.
Free Trade Zones: Dubai’s numerous free trade zones attract foreign direct investment by offering tax incentives, 100% foreign ownership, and streamlined business setup processes.
6. Transportation and Logistics
Dubai Airports: Dubai International Airport and Al Maktoum International Airport are key aviation hubs, connecting travelers and cargo shipments worldwide.
Dubai Logistics Hub: The Dubai Logistics Corridor, which includes ports, airports, and logistics parks, facilitates the efficient movement of goods and services.
7. Innovation and Technology
Dubai Silicon Oasis: This technology park encourages innovation and entrepreneurship in the technology sector, fostering the growth of startups and technology-focused businesses.
Smart Dubai: The Smart Dubai initiative seeks to transform the city into a smart city, harnessing technology to improve public services and enhance the quality of life for residents and visitors.
Must-Visit Attractions
Burj Khalifa: Touching the Sky
The Burj Khalifa is an architectural marvel and the world’s tallest skyscraper. Rising to dizzying heights, it offers breathtaking panoramic views of Dubai from its observation decks. A symbol of Dubai’s ambition and innovation, it stands as an engineering masterpiece that leaves visitors in awe.
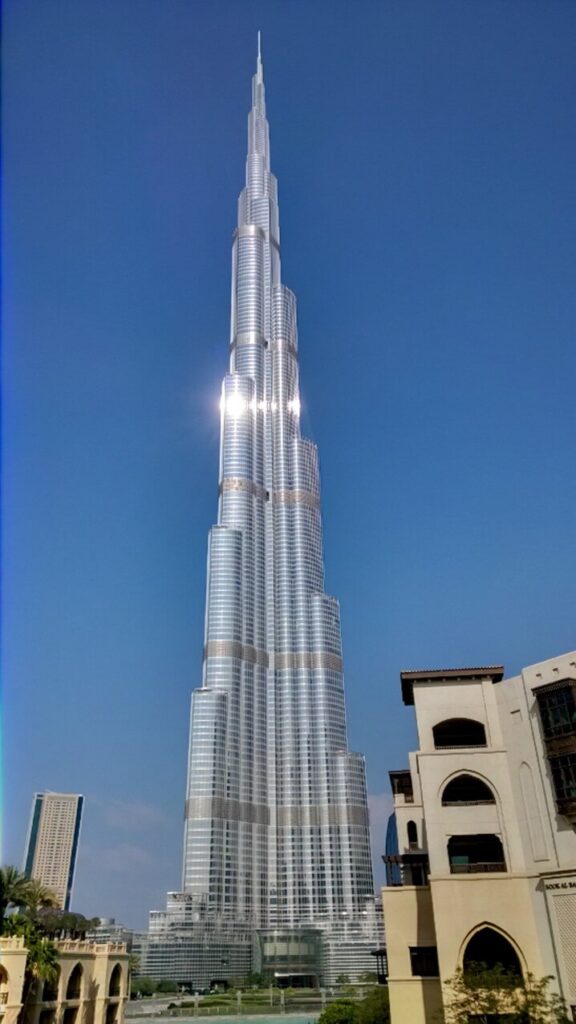

The Palm Jumeirah: Man-made Wonder
Palm Jumeirah, often referred to as the “Eighth Wonder of the World,” is an extraordinary man-made island that stands as an iconic symbol of Dubai’s ambition and innovation. Shaped like a palm tree with a crescent, this architectural marvel is one of the world’s largest artificial islands, extending into the Arabian Gulf.
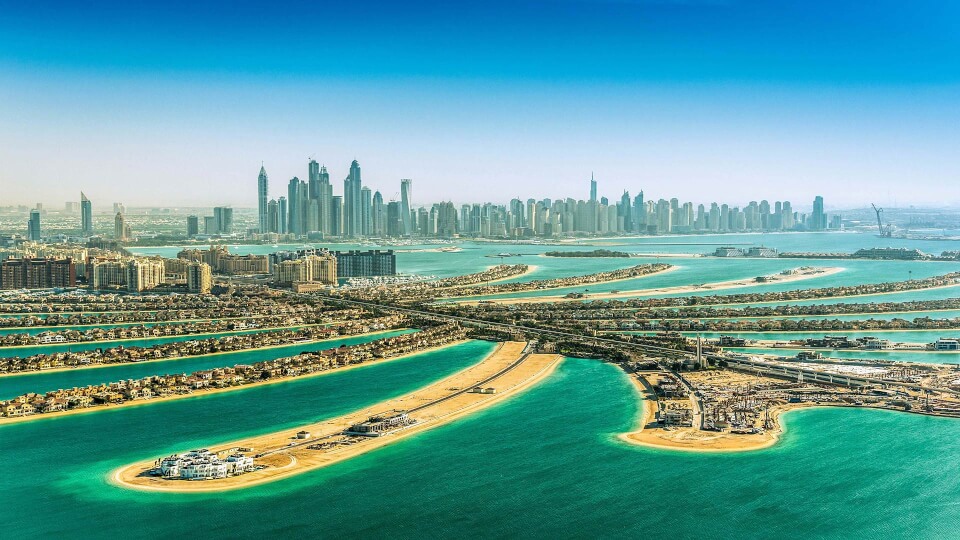

The Palm is renowned for its luxurious resorts, upscale residential villas, and an array of entertainment and dining options. Visitors to this palm-shaped paradise can experience the epitome of opulence, with stunning beachfront views, world-class spa facilities, and an underwater aquarium. Whether you’re looking for a tranquil beach getaway or an exclusive dining experience with breathtaking sea views, Palm Jumeirah offers an unmatched blend of extravagance and natural beauty, making it a must-visit destination in Dubai.
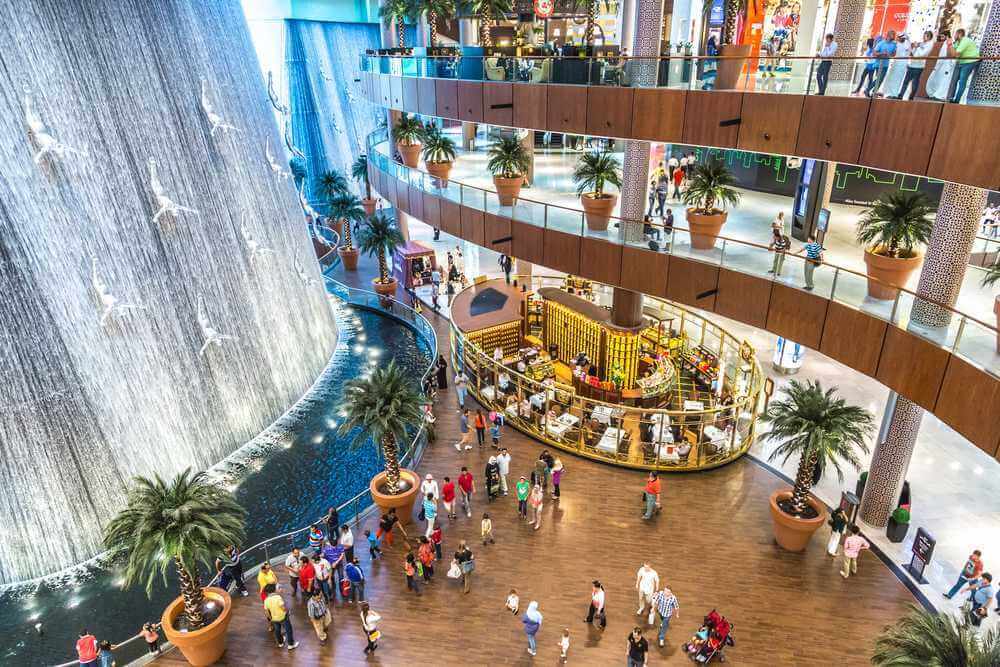
Dubai Mall: Shopper’s Paradise
The Dubai Mall is not just a shopping destination; it’s an entertainment and leisure paradise. With over 1,200 shops, a dazzling array of dining options, and attractions like the Dubai Aquarium and Dubai Fountain, it’s a shopper’s haven and an all-encompassing entertainment complex.

Desert Safari: A Taste of Adventure
Dubai’s desert safaris provide an unforgettable adventure into the Arabian Desert’s mesmerizing dunes. Visitors can experience the thrill of dune bashing, ride camels, enjoy traditional Bedouin hospitality, and witness the desert’s serene beauty under the starlit sky.
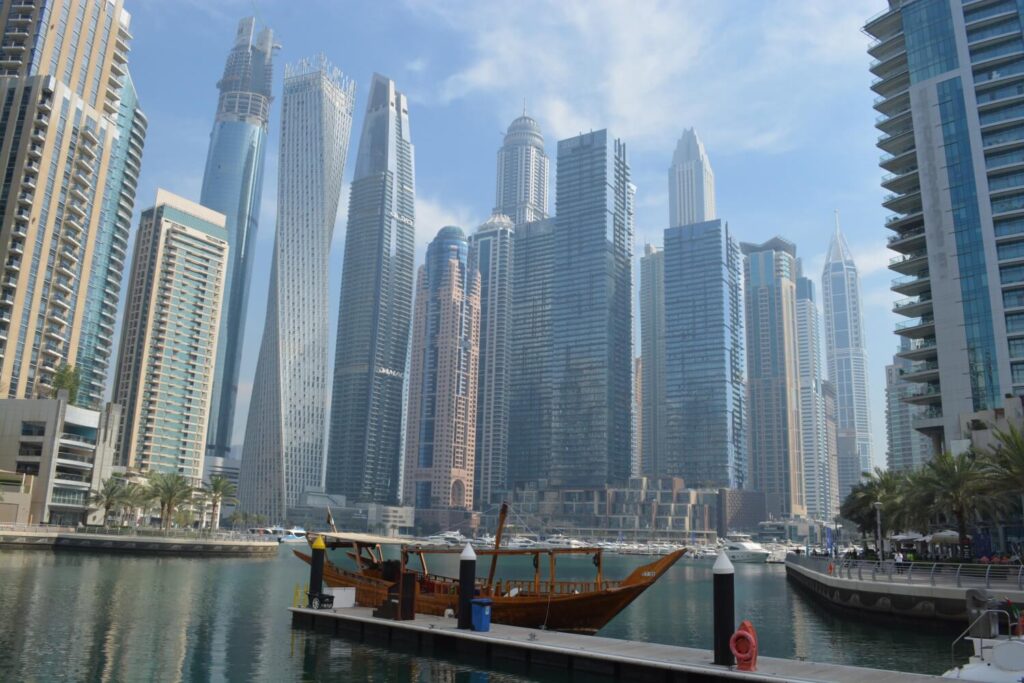
Dubai Marina: City Living by the WaterFront
Dubai Marina is a stunning waterfront district that boasts an array of skyscrapers, luxury yachts, and a picturesque promenade. It’s a lively destination with a vibrant dining and nightlife scene, making it a favorite among both tourists and residents.

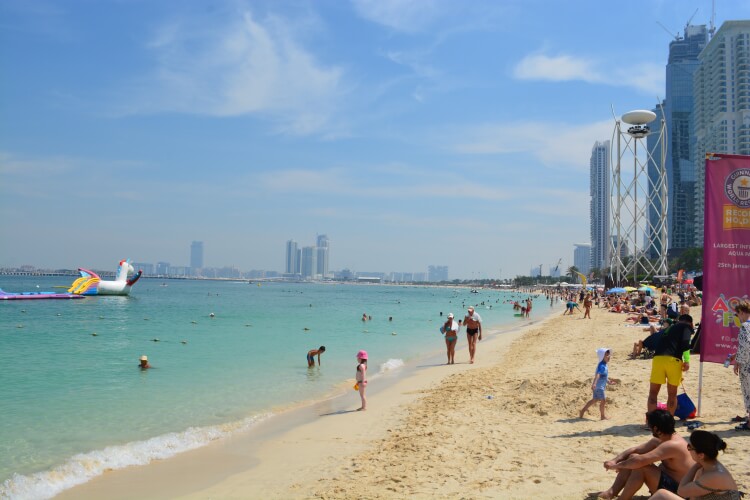
Dubai Beaches: Beautiful Locations to Chill
Dubai’s pristine beaches along the Arabian Gulf offer a tranquil escape from the city’s bustling life. From the popular Jumeirah Beach to the more secluded spots along the Palm Jumeirah, these beaches provide relaxation, water sports, and breathtaking sunsets.

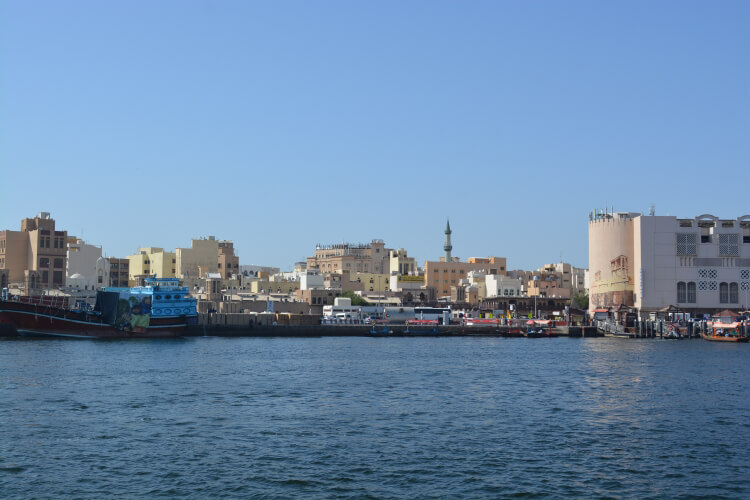
Dubai Creek: The History of Dubai
The historic Dubai Creek divides the city into two distinct districts, Deira and Bur Dubai. It’s not just a natural waterway but also a reflection of Dubai’s heritage. Visitors can take traditional abra boat rides, explore the bustling souks (markets), and immerse themselves in the city’s rich history.

Emirati Culture and Traditions
Traditional Dress and Hospitality
Traditional Emirati dress and hospitality are integral aspects of the rich cultural heritage of Dubai. Emirati men often wear the kandura, a flowing white robe, while women don the abaya, a long, elegant black cloak. These traditional garments not only serve practical purposes in the desert climate but also symbolize modesty and cultural identity.
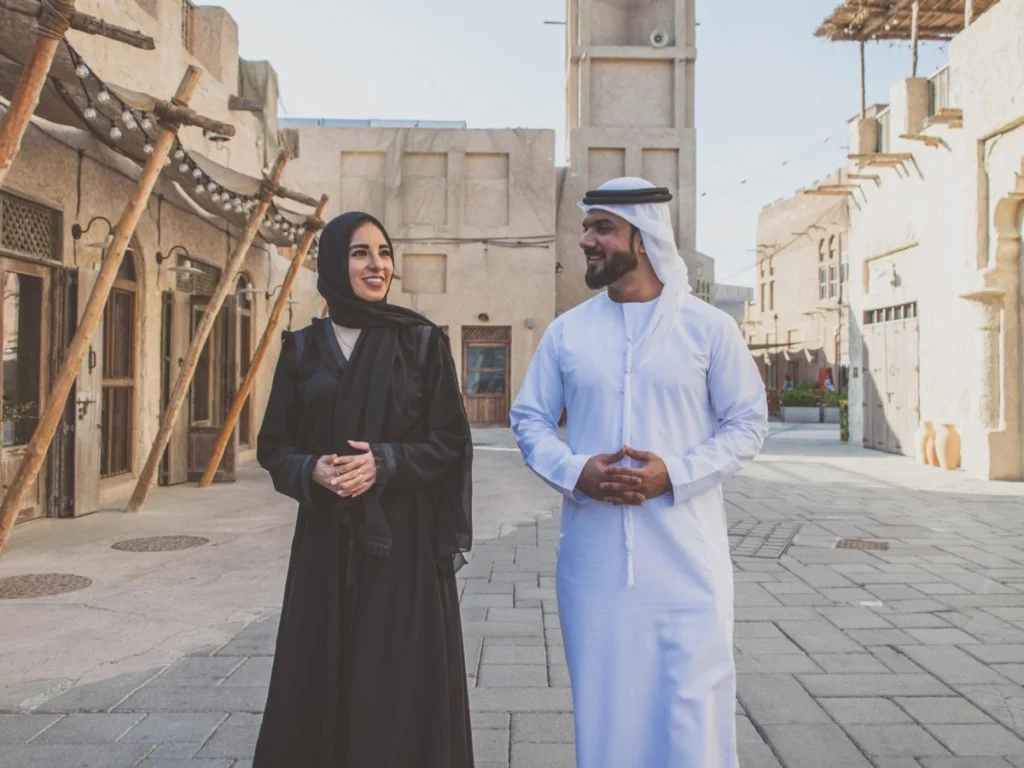

Emiratis are renowned for their warm and welcoming hospitality, exemplified by the custom of offering Arabic coffee (gahwa) and dates to guests. Majlis gatherings, where people come together to share stories and engage in discussions, are a testament to the Emirati spirit of camaraderie. Visitors to Dubai are often greeted with open arms, ensuring that they experience the genuine warmth of Emirati culture and traditions during their stay.
Arabic Cuisine: A Gastronomic Journey
Arabic cuisine is a culinary journey that tantalizes the senses and reflects the rich cultural tapestry of Dubai and the wider UAE. Known for its bold flavors, aromatic spices, and hearty dishes, Arabic cuisine is a delightful fusion of tradition and innovation. One of the most iconic dishes is shawarma, succulent slices of seasoned meat wrapped in warm flatbread and often accompanied by tahini sauce and fresh vegetables.
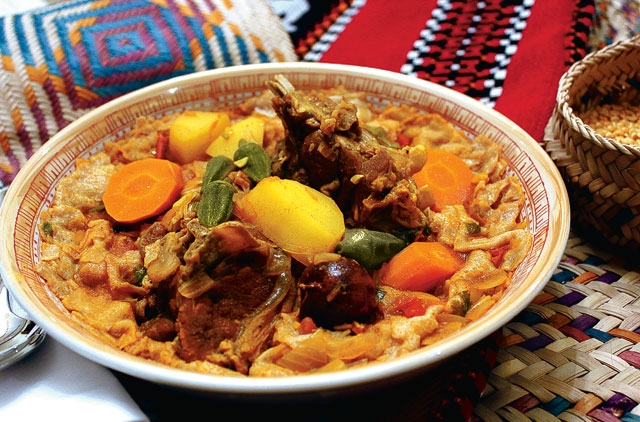

Another beloved dish is falafel, crispy chickpea patties that are both flavorful and vegetarian-friendly. For those seeking an indulgent experience, Arabic cuisine offers dishes like biryani, a fragrant rice dish with tender meat, and kunafa, a delectable dessert made with layers of crunchy pastry and sweet syrup. With a wide array of mezze (appetizers) featuring hummus, tabbouleh, and baba ghanoush, Arabic cuisine invites diners to savor a diverse range of flavors while embracing the warm hospitality that is synonymous with Dubai’s culinary culture.
Festivals and Celebrations
Festivals and celebrations in Dubai are a vibrant testament to the city’s cultural diversity and spirit of inclusivity. While Dubai primarily follows Islamic traditions, it welcomes people from all over the world, making it a melting pot of cultures and celebrations. Islamic festivals like Eid Al Fitr and Eid Al Adha are celebrated with grandeur, uniting families and communities for prayers, feasts, and joyous festivities. Dubai’s multicultural population also marks various international festivals, including Diwali, Christmas, and Chinese New Year, with enthusiasm, colorful displays, and special events.
The Dubai Shopping Festival and Dubai Summer Surprises are annual retail extravaganzas that feature discounts, entertainment, and fireworks, attracting shoppers and tourists alike. Additionally, Dubai hosts cultural festivals, such as the Dubai International Film Festival and Dubai Jazz Festival, showcasing international talent and fostering appreciation for the arts. These celebrations reflect Dubai’s commitment to diversity, tolerance, and the promotion of cultural exchange, making the city a year-round hub of festivity and cultural enrichment.
Living and Visiting Dubai: Essential Guidelines
Visa and Entry Requirements
Dubai’s visa and entry requirements are essential considerations for anyone planning to visit this remarkable city. The specific requirements can vary based on your nationality, the purpose of your visit, and the duration of your stay. Typically, visitors from many countries can obtain a tourist visa on arrival at Dubai International Airport, allowing for a stay of up to 30 days, which can be extended for an additional 30 days.

However, it’s crucial to check the latest visa regulations and entry requirements before travelling, as they are subject to change. Some nationalities may require advance visa applications, while others may benefit from visa exemptions. Additionally, Dubai enforces strict customs regulations, so it’s essential to be aware of what items can and cannot be brought into the country. Travellers are encouraged to have a valid passport, proof of sufficient funds, and a return or onward ticket. Dubai’s entry requirements are designed to ensure a smooth and hassle-free experience for visitors, allowing them to explore and enjoy this vibrant city with ease.
Local Etiquette and Customs
Local etiquette and customs play a significant role in the social fabric of Dubai, and understanding and respecting them is essential for a harmonious experience. Dubai is an Islamic city, and as such, it observes conservative values. Modesty in dress is highly appreciated, particularly in public areas. When visiting mosques or other religious sites, visitors should dress modestly, covering their shoulders and knees. During the holy month of Ramadan, it’s important to refrain from eating, drinking, or smoking in public places during daylight hours as a sign of respect for those fasting.
When greeting others, a polite handshake is common, but it’s crucial to be mindful of cultural sensitivities and to use your right hand, as the left hand is traditionally considered less clean. Additionally, showing respect to elders and local customs, such as removing one’s shoes before entering someone’s home, is a sign of courtesy. Dubai’s society values hospitality, and visitors who embrace these customs will find themselves warmly welcomed and appreciated in this multicultural city.
Safety and Security
Safety and security in Dubai country are top priorities, making it one of the safest cities in the world for residents and tourists alike. The city’s well-trained and efficient police force, along with strict laws and regulations, contribute to a low crime rate. Violent crimes are rare, and visitors can generally explore Dubai with a sense of security and peace of mind.
However, as in any major city, it’s essential to exercise common-sense precautions, such as safeguarding personal belongings and being aware of your surroundings. Dubai also places a strong emphasis on road safety, and the city’s roads are well-maintained and equipped with modern infrastructure. The healthcare system in Dubai is of high quality, ensuring prompt medical assistance if needed. Overall, Dubai’s commitment to safety and security, combined with its welcoming atmosphere, makes it an ideal destination for travellers seeking a safe and enjoyable experience.
Transportation
Transportation in Dubai is renowned for its efficiency, modernity, and convenience, offering a seamless experience for residents and visitors alike. The city boasts an extensive and well-connected public transportation system, including a metro network that covers key areas, buses, trams, and water taxis along the Dubai Creek. The Dubai Metro, in particular, is a standout feature, known for its cleanliness and punctuality, making it a popular choice for getting around the city.
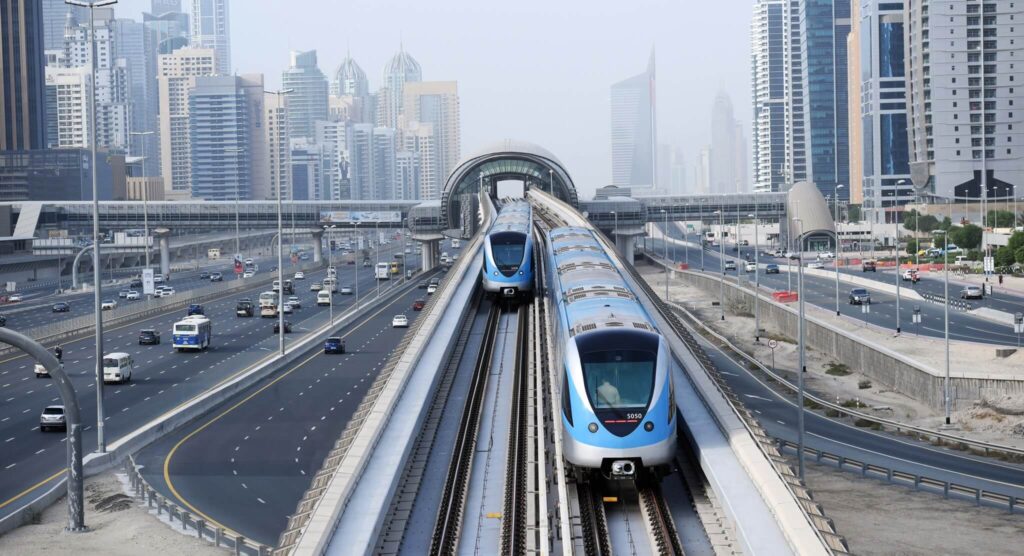

Taxis are readily available and are regulated to ensure safety and reliability. Additionally, ride-sharing services like Uber and Careem are widely used. For those who prefer to drive, Dubai’s well-maintained road infrastructure and clear signages make it easy to navigate. The city is also working toward a futuristic transportation system, including the development of hyperloop technology and autonomous vehicles. Dubai’s commitment to innovation and efficiency in transportation ensures that moving around the city is a breeze, allowing visitors to explore its many attractions with ease and comfort.
Beyond the Skyscrapers: Hidden Gems
Transportation in Dubai country is renowned for its efficiency, modernity, and convenience, offering a seamless experience for residents and visitors alike. The city boasts an extensive and well-connected public transportation system, including a metro network that covers key areas, buses, trams, and water taxis along the Dubai Creek. The Dubai Metro, in particular, is a standout feature, known for its cleanliness and punctuality, making it a popular choice for getting around the city.
Taxis are readily available and are regulated to ensure safety and reliability. Additionally, ride-sharing services like Uber and Careem are widely used. For those who prefer to drive, Dubai’s well-maintained road infrastructure and clear signages make it easy to navigate. The city is also working toward a futuristic transportation system, including the development of hyperloop technology and autonomous vehicles. Dubai’s commitment to innovation and efficiency in transportation ensures that moving around the city is a breeze, allowing visitors to explore its many attractions with ease and comfort.
Video Tour
Conclusion
In conclusion, Dubai country stands as a remarkable testament to human ambition and innovation. From its humble origins as a desert trading post to its current status as a global metropolis, Dubai’s journey is one of transformation, resilience, and boundless aspiration. Its iconic skyline, world-class infrastructure, and commitment to diversification have made it a dynamic hub for business, tourism, and culture.
Yet, beyond the glittering skyscrapers, Dubai’s heart lies in its rich heritage, warm hospitality, and commitment to inclusivity. It is a city where tradition and modernity coexist harmoniously, inviting visitors to explore a diverse tapestry of experiences, from ancient souks to cutting-edge attractions. Dubai’s story is one of endless possibilities, where dreams take flight and where the future is not just envisioned but built.
It’s just not a country!
FAQ
Q: What is the best time to visit Dubai?
- A: The best time to visit Dubai is during the winter months, from November to April, when the weather is pleasant and ideal for outdoor activities.
Q: Do I need a visa to visit Dubai?
- A: It depends on your nationality and the purpose of your visit. Many nationalities can obtain a tourist visa on arrival, while others may require advance visa arrangements.
Q: What currency is used in Dubai?
- A: The official currency of Dubai is the UAE Dirham (AED).
Q: Is it safe to travel to Dubai?
- A: Yes, Dubai is considered one of the safest cities in the world for travellers. Violent crime is rare, and the city prioritizes safety and security.
Q: Can I drink alcohol in Dubai?
- A: Alcohol is available in Dubai but is regulated. It can be consumed in licensed venues, such as hotels, bars, and clubs.
Q: What is the legal drinking age in Dubai?
- A: The legal drinking age in Dubai is 21 years old.
Q: Is it mandatory to dress modestly in Dubai?
- A: While there is no strict dress code for tourists, it is advisable to dress modestly in public areas and when visiting religious sites.
Q: Can I use my credit card in Dubai?
- A: Yes, credit cards are widely accepted in Dubai. It is a convenient mode of payment in most establishments.
Q: What are the popular tourist attractions in Dubai?
- A: Some of the top attractions in Dubai include the Burj Khalifa, Dubai Mall, Palm Jumeirah, Desert Safaris, and Dubai Creek.
Q: Are there cultural events and festivals in Dubai?
- A: Yes, Dubai hosts various cultural festivals and events throughout the year, including the Dubai Shopping Festival, Dubai International Film Festival, and traditional celebrations like Eid Al Fitr and Eid Al Adha.
Useful Links
- More information about Dubai Country.
- More details about Dubai Entry Requirements for Visitors.
- Another guide to Dubai.
- Take a look at the history of Dubai through Dubai Creek.
- The Burj Khalifa is one of the true icons of Dubai.
- The Dubai Mall, the Mall of the Emirates, and Dubai Hills Mall are great shopping experiences.
- The Palm Jumeirah is the ultimate Dubai icon.
- The best beaches in Dubai can be found here.
- Love history? Check out the Al Fahidi Historical Neighborhood.
- This is a great Dubai Travel Itinerary for different time periods visiting Dubai.
- The Expo City Dubai is a new and exciting addition to Dubai’s landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Location: Dubai Country is located in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. It is known for its strategic location as a major global transportation hub. But it is not a country, it is an Emirate of the UAE.
- Skyscrapers: Dubai is famous for its impressive skyline filled with towering skyscrapers, including the iconic Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest building.
- Luxury and Opulence: Dubai is synonymous with luxury, offering high-end shopping, extravagant hotels, and luxurious lifestyles. The city is home to some of the world’s most luxurious brands and establishments.
- Economic Hub: It has rapidly transformed into a major financial and business hub in the Middle East, attracting multinational corporations and entrepreneurs from around the world.
- Tourism: Dubai is a top tourist destination known for its lavish resorts, beautiful beaches, and unique attractions such as the Palm Jumeirah and the Dubai Fountain.
- Diverse Culture: Despite its modern image, Dubai has a diverse population with a blend of cultures from around the world, making it a melting pot of traditions and languages.
- Tax-Free Income: Dubai’s tax-free income policies have made it an attractive destination for expatriates seeking employment and business opportunities.
- Infrastructure: The city boasts state-of-the-art infrastructure, including an efficient public transportation system, world-class airports, and modern road networks.
- Shopping: Dubai is famous for its shopping festivals and malls, including the Dubai Mall, one of the largest shopping centers in the world.
- Cultural Heritage: While known for its modernity, Dubai also values its cultural heritage. Visitors can explore historical sites such as Al Fahidi Historic Neighborhood and the Dubai Museum.
- Hospitality: Dubai Country is renowned for its hospitality and is a host city for numerous international conferences, events, and exhibitions.
- Cuisine: The city offers a wide range of culinary experiences, from traditional Arabic dishes to international cuisine served in various restaurants and street food stalls.
- Desert Adventures: Beyond the city, the Arabian Desert provides opportunities for desert safaris, sandboarding, and camel riding.
- Sustainable Initiatives: Dubai Country has launched various sustainability initiatives, including solar power projects and the Dubai Sustainable City, to reduce its environmental impact.
- Global Connectivity: Dubai International Airport is one of the busiest in the world, connecting travelers to various destinations across the globe.
- Art and Culture: The city has a growing art and cultural scene, with institutions like the Dubai Opera and Art Dubai contributing to its cultural vibrancy.
- Religious Tolerance: Dubai promotes religious tolerance, with various places of worship for different faiths, making it a welcoming destination for people from diverse backgrounds.
- Safety: Dubai is known for its low crime rate and is considered a safe destination for tourists and residents.
- Visionary Leadership: The rapid development of Dubai can be attributed to the visionary leadership of its rulers, who have implemented ambitious plans for the city’s growth.
These key takeaways highlight some of the many facets that make Dubai Country a unique and dynamic city. It’s a place where tradition and modernity coexist, offering visitors a wide range of experiences and opportunities.





