
Introduction
Dubai, a vibrant city located in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), is not only known for its stunning architecture and luxurious lifestyle but also for its thriving economy. Over the years, Dubai has transformed itself into a global business hub, attracting investors, entrepreneurs, and professionals from around the world. The Dubai Economy is strong and robust, seeing off economic problems such as the Covid-19 pandemic.
If you are coming to visit Dubai or looking to stay, then this post may be of interest to you. In this article, we will explore the dynamic nature of the Dubai economy, its major industries, legal frameworks, international trade, and the challenges it faces. So let’s dive in and unravel the economic landscape of Dubai.
Table Of Contents
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and other Statistics
Legal Frameworks and Regulation
Dubai International Financial Center (DIFC)
History of the Dubai Economy
Dubai’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has been consistently growing over the years, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. The city’s GDP is primarily driven by various sectors, including real estate, construction, finance, and tourism. In recent years, Dubai’s GDP has shown resilience despite global economic challenges. Additionally, key economic indicators such as foreign direct investment, employment rates, and consumer spending contribute to the overall economic health of the city.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and other Economic Indicators
Dubai’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is lined to the UAE and has been consistently growing over the years, making it one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. The country’s GDP is primarily driven by various sectors, including real estate, construction, finance, and tourism.
In recent years, the UAE’s GDP has shown resilience despite global economic challenges. Additionally, key economic indicators such as foreign direct investment, employment rates, and consumer spending contributed to the overall economic health of the city.
The data shown below is indicative and the exact figures are available from the relevant government sources. See Useful Links below.
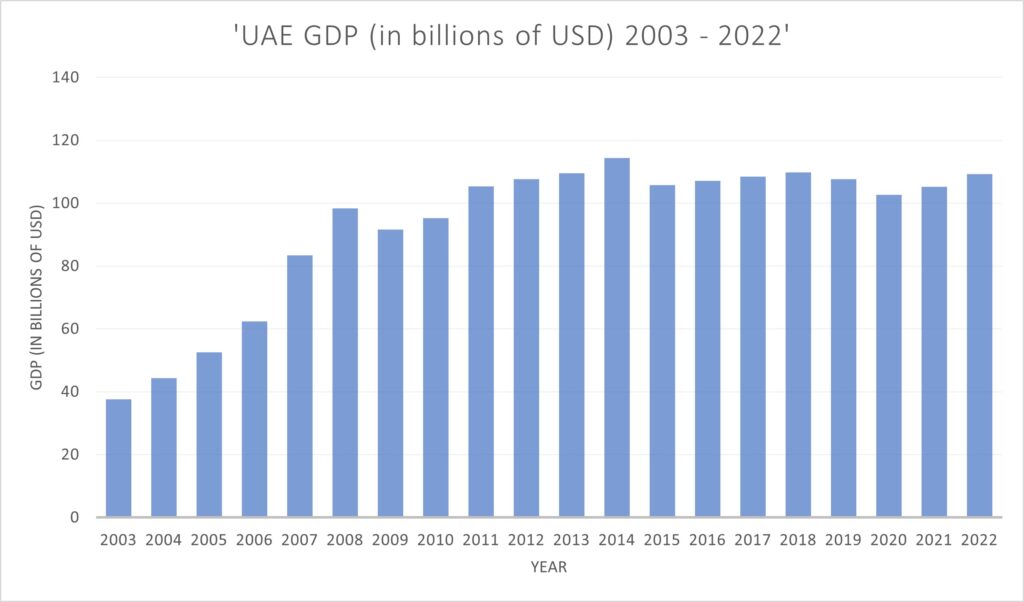
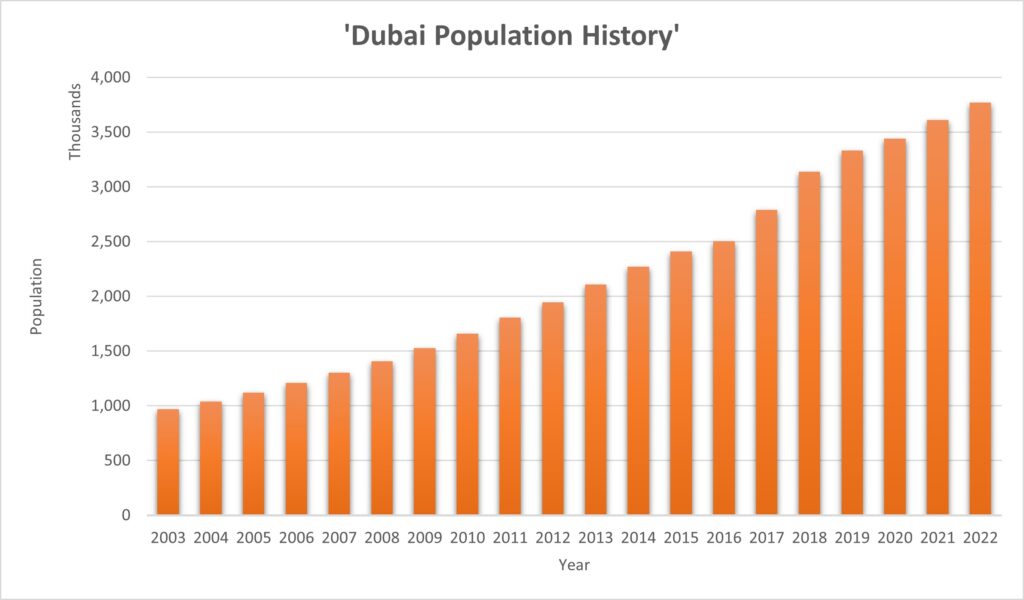
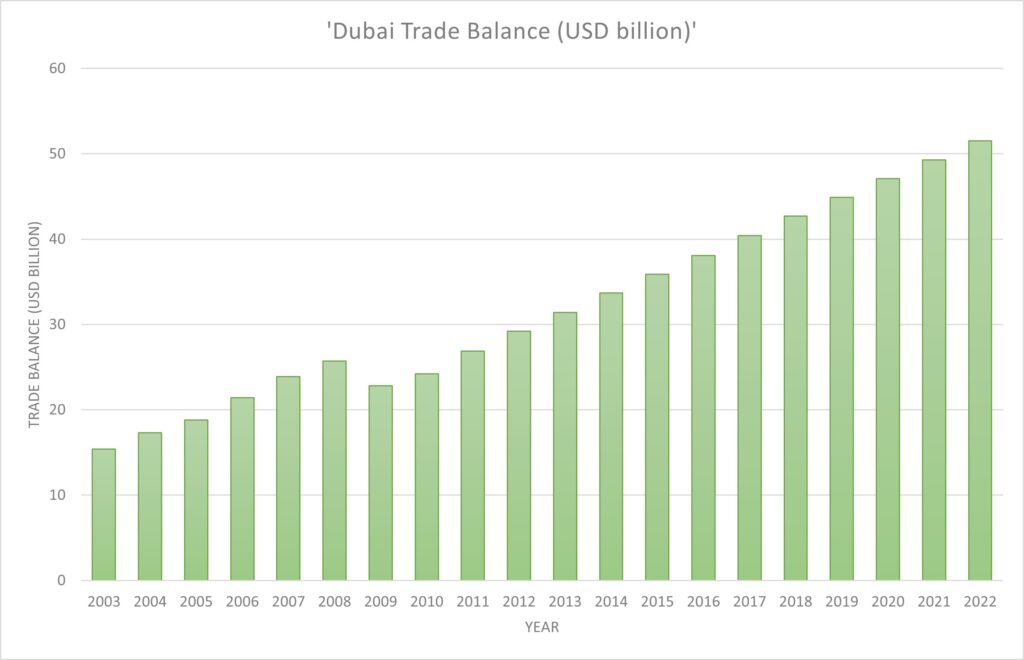
Dubai has survived remarkably well through turbulent periods such as the Covid-19 outbreak and worldwide economic recessions such as in 2008 – 2010. This demonstrates the robustness of the economic vision and the investment that has been made in the state for the long term.
The graphs above demonstrate the ongoing long-term growth of Dubai and its economy despite the small-term hits during worldwide economic downturns.
Major Industries
Historically Dubai had relied on its revenues from oil and gas, but in recent decades there has been a huge movement to diversify the economy which is reflected in new industries such as tourism, construction, and real estate. This strategy continues with large investments now to grow the IT sector, financial services, healthcare, education, and logistics. We can expect this strategy to continue over the long term.
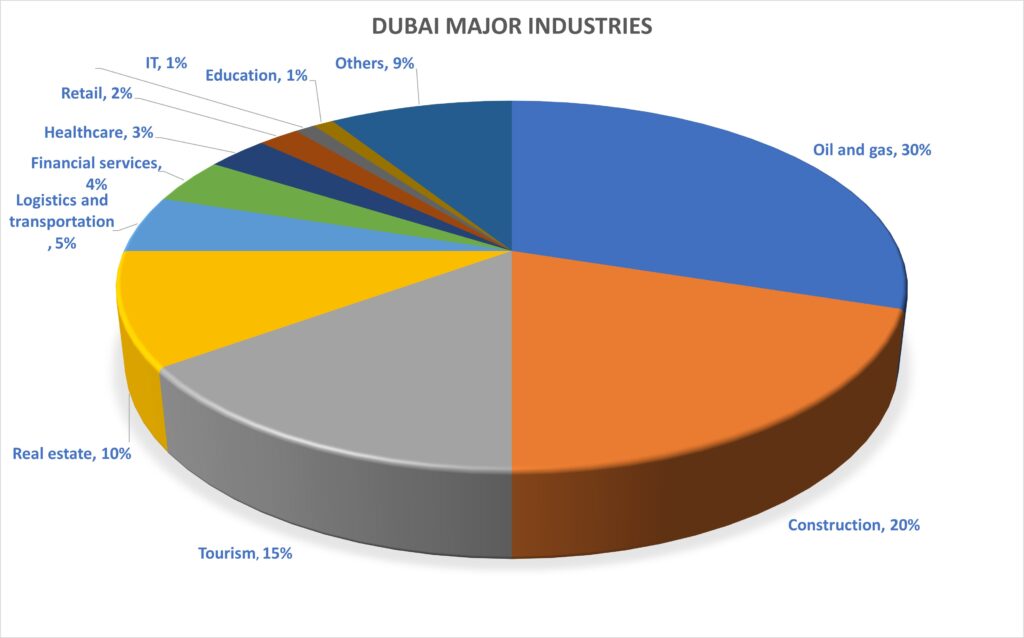
Let’s take a look in more detail at some of the major industrial sectors in Dubai.
Wholesale and Retail Trade
Wholesale and retail trade play significant roles in Dubai’s economy, contributing to its vibrant business landscape. These sectors encompass a wide range of activities, from buying and selling goods to distribution and marketing. Let’s explore wholesale and retail trade in Dubai in more detail:

1. Wholesale Trade: Wholesale trade in Dubai involves the purchasing of goods in large quantities from manufacturers, producers, or importers, and then selling them to retailers, businesses, or other intermediaries. The wholesale sector acts as a link between producers and retailers, ensuring the smooth flow of goods within the supply chain. Key aspects of wholesale trade in Dubai include:
a. Distribution and Logistics: Dubai’s strategic location and well-developed infrastructure make it a prime hub for distribution and logistics. The wholesale sector plays a vital role in warehousing, inventory management, and transportation, facilitating the efficient movement of goods both domestically and internationally.
b. Import and Export: Dubai’s international trade connections and free trade zones make it an ideal location for import and export activities. Wholesale traders in Dubai engage in the import of goods from various countries and subsequently distribute them to local retailers or export them to other markets.
c. Wholesale Markets and Free Zones: Dubai hosts several wholesale markets and free zones that specialize in specific industries or product categories. Examples include the Dubai Textile City, Dubai Fruit and Vegetable Market, and Dubai Gold and Diamond Park. These dedicated wholesale hubs attract local and international traders, fostering a competitive and diverse wholesale trade environment.
2. Retail Trade: Retail trade in Dubai involves the final sale of goods to consumers for personal use or consumption. The retail sector caters to a broad range of consumer needs, offering diverse products and services in various formats. Key aspects of retail trade in Dubai include:
a. Shopping Malls and Retail Centers: Dubai is renowned for its extensive shopping malls and retail centers, offering a wide range of products, from luxury brands to affordable goods. These retail destinations attract locals, residents, and tourists alike, creating a vibrant retail landscape and contributing significantly to Dubai’s economy.
b. Diverse Retail Formats: Retail in Dubai encompasses various formats, including department stores, specialized boutiques, supermarkets, hypermarkets, convenience stores, and e-commerce platforms. The retail sector caters to different consumer preferences, providing a diverse shopping experience for residents and visitors.
c. Tourism and Duty-Free Shopping: Dubai’s thriving tourism industry plays a crucial role in the retail sector. Tourists flock to Dubai for its shopping opportunities, including duty-free shopping at airports, malls, and souks. Duty-free retail contributes significantly to the retail trade, offering tax-free shopping for visitors.
d. E-commerce and Digital Retail: With the rise of digital technology, e-commerce has gained prominence in Dubai’s retail landscape. Online shopping platforms and digital retail channels provide convenience and accessibility to consumers, allowing them to shop from the comfort of their homes.
Both wholesale and retail trade sectors in Dubai are regulated by the Department of Economic Development (DED), which ensures fair trade practices, consumer protection, and the issuance of trade licenses. These sectors contribute to job creation, drive economic growth, and enhance Dubai’s status as a global shopping destination.

Transport and Logistics
Transport and logistics trade plays a crucial role in Dubai’s economy, contributing to its position as a global transportation and logistics hub. Dubai’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa, coupled with its well-developed infrastructure and business-friendly environment, has made it an ideal destination for transport and logistics activities. Let’s explore the transport and logistics trade in Dubai in more detail:
1. Transportation Infrastructure: Dubai boasts world-class transportation infrastructure, including airports, seaports, roads, and railways. These facilities facilitate the efficient movement of goods and people, both domestically and internationally. Key aspects of transportation infrastructure in Dubai include:
a. Airports: Dubai is home to Dubai International Airport (DXB) and Al Maktoum International Airport (DWC). DXB is one of the busiest airports globally, serving as a major connecting hub for passengers and cargo. DWC, also known as Dubai World Central, is a dedicated cargo airport with extensive cargo handling capabilities.
b. Seaports: Jebel Ali Port and Port Rashid are Dubai’s primary seaports. Jebel Ali Port is one of the largest container ports globally and serves as a key transshipment hub. These seaports enable efficient import and export activities, handling a wide range of cargo, including containers, bulk cargo, and project cargo.

c. Roads and Railways: Dubai has an extensive road network and well-maintained highways, connecting the city to other emirates within the UAE and neighboring countries. The Dubai Metro, comprising both metro and tram systems, provides a convenient mode of transportation for residents and visitors.
2. Freight and Logistics Services: Dubai’s logistics sector encompasses a wide range of services, facilitating the movement of goods across various industries. Key aspects of the freight and logistics services in Dubai include:
a. Freight Forwarding: Dubai is home to numerous freight forwarding companies that specialize in coordinating the movement of goods, including customs clearance, documentation, and transportation. These companies play a crucial role in international trade, ensuring the efficient and timely delivery of goods.
b. Warehousing and Distribution: The logistics sector in Dubai offers comprehensive warehousing and distribution services. Warehouses in Dubai cater to various industries, including general cargo, perishables, e-commerce, and cold storage. Efficient distribution networks ensure that goods are delivered to their intended destinations promptly.
c. Third-Party Logistics (3PL): Dubai has a well-established third-party logistics industry, providing integrated logistics services to businesses. 3PL companies offer services such as inventory management, order fulfillment, packaging, and transportation, enabling businesses to focus on their core operations.
3. Free Trade Zones: Dubai’s free trade zones, such as Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA) and Dubai South, have played a significant role in attracting transport and logistics companies. These free zones offer numerous benefits, including tax advantages, 100% foreign ownership, and streamlined customs procedures, making them ideal locations for logistics operations.
4. E-commerce and Last-Mile Delivery: The rise of e-commerce has transformed the transport and logistics trade in Dubai. With the growth of online shopping, last-mile delivery services have become increasingly important. Dubai’s logistics sector has adapted to meet the demands of e-commerce, ensuring efficient delivery of packages to customers’ doorsteps.

Dubai’s government, through entities like the Dubai Maritime City Authority (DMCA) and Dubai Customs, plays a vital role in regulating and promoting the transport and logistics trade. By investing in infrastructure development, creating business-friendly policies, and fostering innovation, Dubai has positioned itself as a global leader in the transport and logistics sector, attracting international businesses and driving economic growth.
Banking, Insurance, and Capital Markets
Banking, insurance, and capital markets form a crucial part of Dubai’s financial services sector, contributing significantly to the city’s economy. With a robust regulatory framework, favorable business environment, and strategic location, Dubai has emerged as a leading financial hub in the Middle East. Let’s explore each of these sectors in more detail:

1. Banking: Dubai’s banking sector is well-developed, offering a wide range of financial services to individuals, businesses, and institutions. Key aspects of the banking sector in Dubai include:
a. Local and International Banks: Dubai is home to both local and international banks, catering to the diverse financial needs of its residents and businesses. Local banks play a significant role in providing traditional banking services, such as retail banking, corporate banking, and wealth management. International banks have established a strong presence in Dubai, leveraging its strategic location to serve regional and global clients.
b. Islamic Banking: Dubai has gained prominence as a hub for Islamic banking and finance. These banks operate in compliance with Sharia principles, offering a range of products and services that adhere to Islamic law. This type of finance has seen significant growth in Dubai, attracting investors seeking Sharia-compliant banking solutions.
c. Digital Banking and Fintech: Dubai’s banking sector has embraced digitalization and fintech innovations. Banks offer digital banking services, allowing customers to conduct transactions, manage accounts, and access financial services through online and mobile platforms. Fintech startups have also emerged, offering innovative solutions in areas like payments, lending, and financial technology.
2. Insurance: Dubai’s insurance sector plays a vital role in providing risk management and protection to individuals and businesses. Key aspects of the insurance sector in Dubai include:
a. General and Life Insurance: The insurance market in Dubai offers a wide range of general insurance products, including motor, property, and liability insurance. Life insurance and personal insurance products, such as health and critical illness coverage, are also available. Insurance companies in Dubai provide coverage for individuals, businesses, and specialized sectors like marine and aviation.
b. Reinsurance: Dubai has developed a strong reinsurance market, attracting both local and international reinsurers. Reinsurance companies provide coverage to primary insurance companies, helping them manage risks and stabilize their operations.
c. Takaful Insurance: Takaful, or Islamic insurance, is an important segment of the insurance industry in Dubai. It follows the principles of mutual cooperation and shared responsibility in providing insurance coverage. These companies offer Sharia-compliant insurance products and services to individuals and businesses.
3. Capital Markets: Dubai’s capital markets provide avenues for raising capital, investment opportunities, and trading of financial instruments. Key aspects of the capital markets in Dubai include:
a. Dubai Financial Market (DFM): The DFM is one of the leading stock exchanges in the region, facilitating the listing and trading of equities and other securities. It provides a platform for companies to raise capital and offers investment opportunities for individual and institutional investors.
b. NASDAQ Dubai: NASDAQ Dubai is a specialized stock exchange that focuses on equity listings and trading of regional and international companies. It offers a platform for companies to access regional and international investors and provides a gateway for global investors to invest in the Middle East.
c. Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC): DIFC is a financial free zone in Dubai that hosts a wide range of financial institutions, including banks, insurance companies, asset management firms, and capital market participants. It has its own regulatory framework and provides a business-friendly environment for conducting financial services and capital market activities.
Dubai’s government, through entities like the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) and Dubai International Financial Centre Authority (DIFCA), ensures the regulation and supervision of the banking, insurance, and capital markets sectors. By fostering innovation, attracting international players, and providing a secure and transparent financial ecosystem, Dubai has established itself as a thriving financial center in the region.

Manufacturing
The manufacturing market in Dubai plays a significant role in the city’s economic diversification and industrial development. While Dubai is well-known for its service-based economy, the manufacturing sector has been steadily growing, contributing to job creation, export opportunities, and technological advancements. Let’s explore the manufacturing market in Dubai in more detail:
1. Industrial Zones and Infrastructure: Dubai has established dedicated industrial zones and infrastructure to support manufacturing activities. These zones provide specialized facilities, incentives, and a favorable business environment for manufacturing companies. Key industrial zones in Dubai include:
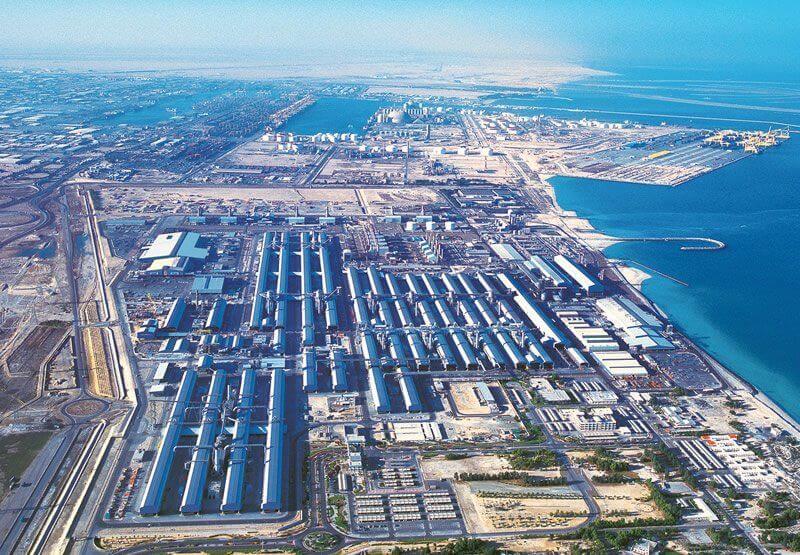

a. Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA): JAFZA is one of the largest free zones in the world, hosting numerous manufacturing companies across various sectors. It offers advantages such as tax exemptions, customs privileges, and world-class infrastructure.
b. Dubai Industrial City (DIC): DIC focuses on heavy industries, including manufacturing, logistics, and assembly. It provides industrial land, warehouses, and manufacturing facilities, catering to diverse industries such as automotive, construction, food processing, and more.
c. Dubai South: Located near Al Maktoum International Airport, Dubai South is a master-planned development that includes logistics, aviation, and manufacturing zones. It offers infrastructure and support for manufacturing companies looking to establish their operations in Dubai.
2. Key Manufacturing Sectors: Dubai’s manufacturing sector spans a wide range of industries. Some of the key manufacturing sectors in Dubai include:
a. Food Processing: Dubai has a strong food processing industry, with companies involved in the production, processing, packaging, and distribution of food and beverages. This sector includes activities such as dairy processing, bakery, confectionery, meat processing, and beverage manufacturing.
b. Construction and Building Materials: The construction sector in Dubai drives the demand for building materials, resulting in a thriving manufacturing industry for construction-related products. Companies in this sector produce materials like cement, steel, aluminum, glass, and plastic products used in construction projects.
c. Electronics and Electrical Equipment: Dubai’s manufacturing market includes electronics and electrical equipment production. This sector encompasses the manufacturing of consumer electronics, electrical appliances, telecommunications equipment, and electronic components.
d. Chemicals and Plastics: Dubai has a growing chemicals and plastics manufacturing industry, producing a wide range of products, including chemicals, polymers, plastics, and plastic packaging materials. These products cater to various industries such as packaging, construction, automotive, and healthcare.
e. Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices: Dubai has seen the emergence of pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing companies. These companies produce pharmaceutical products, medical devices, and healthcare supplies to meet the growing demand in the region.
3. Manufacturing Excellence and Innovation: Dubai’s manufacturing market emphasizes excellence, innovation, and advanced technologies. The government encourages research and development, innovation, and the adoption of smart manufacturing practices. Companies are encouraged to invest in automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, and other advanced manufacturing technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and product quality.
4. Export Opportunities: The manufacturing market in Dubai provides opportunities for both domestic consumption and export. Companies in Dubai can leverage its strategic location, well-developed infrastructure, and global trade connections to access regional and international markets. Dubai’s well-connected transportation networks, including airports, seaports, and road networks, facilitate the efficient movement of manufactured goods.
Dubai’s government supports the manufacturing sector through various initiatives, policies, and incentives to attract investment and stimulate growth. By diversifying its economy and focusing on manufacturing excellence, Dubai aims to establish itself as a regional manufacturing hub, promoting economic sustainability and technological advancement.
Real Estate
The real estate market in Dubai has been a prominent driver of economic growth and development. Known for its iconic skyline and ambitious real estate projects, Dubai has experienced significant growth in its real estate sector over the years. The market offers a range of residential, commercial, and mixed-use properties, attracting both local and international investors. Let’s explore the real estate market in Dubai in more detail:

1. Residential Real Estate: Dubai’s residential real estate market offers a diverse range of properties, including apartments, villas, townhouses, and gated communities. Key aspects of the residential real estate market in Dubai include:
a. Property Types: Dubai’s residential market caters to various preferences and budgets, ranging from luxury properties in prime locations to affordable housing options. The market offers both freehold and leasehold properties, providing opportunities for investors and tenants alike.
b. Developments and Communities: Dubai features numerous residential developments and communities that offer different lifestyles and amenities. From waterfront properties to gated communities with extensive facilities, residents have a wide range of options to choose from.
c. Rental Market: Dubai has a thriving rental market, with a significant number of residents opting to rent properties. Rental yields can vary depending on factors such as location, property type, and market conditions.

2. Commercial Real Estate: Dubai’s commercial real estate market is dynamic and diverse, catering to the needs of various industries and businesses. Key aspects of the commercial real estate market in Dubai include:
a. Office Spaces: Dubai offers a wide range of office spaces, from high-rise buildings in business districts to co-working spaces and flexible office solutions. The city’s business-friendly environment, infrastructure, and connectivity make it an attractive location for local and international companies.
b. Retail Spaces: Dubai’s retail market is vibrant, with numerous shopping malls, retail centers, and high-street destinations. It attracts global brands, luxury retailers, and a thriving mix of local businesses, catering to the diverse shopping preferences of residents and tourists.
c. Industrial and Warehousing Facilities: Dubai’s industrial real estate sector provides facilities for manufacturing, logistics, and warehousing. Industrial zones offer dedicated spaces for various industries, supporting the city’s economic diversification and trade activities.
3. Real Estate Investments: Dubai’s real estate market has been a magnet for investors, both domestic and international. Key aspects of real estate investments in Dubai include:
a. Freehold Ownership: Dubai allows foreign investors to acquire freehold ownership of certain properties in designated areas. This policy has attracted a significant influx of international investors seeking long-term property ownership.
b. Investment Zones: Dubai has established investment zones, such as Dubai Marina, Downtown Dubai, Jumeirah Lake Towers, and Business Bay, that offer attractive investment opportunities. These zones provide infrastructure, amenities, and potential for capital appreciation.
c. Real Estate Financing: Dubai has a well-developed real estate financing sector, with banks and financial institutions providing mortgage and loan facilities to individuals and investors. The availability of financing options has facilitated property purchases and investments.
4. Real Estate Regulations and Governance: Dubai’s real estate market is regulated by the Dubai Land Department (DLD) and the Real Estate Regulatory Agency (RERA). These authorities ensure transparency, regulate property transactions, and safeguard the rights of investors, buyers, and sellers. The regulatory framework enhances investor confidence and protects the integrity of the market.
Dubai’s government continues to focus on developing sustainable real estate projects, enhancing market transparency, and promoting innovative initiatives. The real estate market in Dubai remains a vital sector driving economic growth, attracting investments, and contributing to the city’s iconic skyline and urban development.
Construction
The construction market in Dubai has been a vital sector driving the city’s rapid urban development and infrastructure growth. Known for its ambitious construction projects and futuristic skyline, Dubai has been a global hub for architectural innovation and engineering excellence. The construction market encompasses a wide range of activities, including residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects. Let’s explore the construction market in Dubai in more detail:
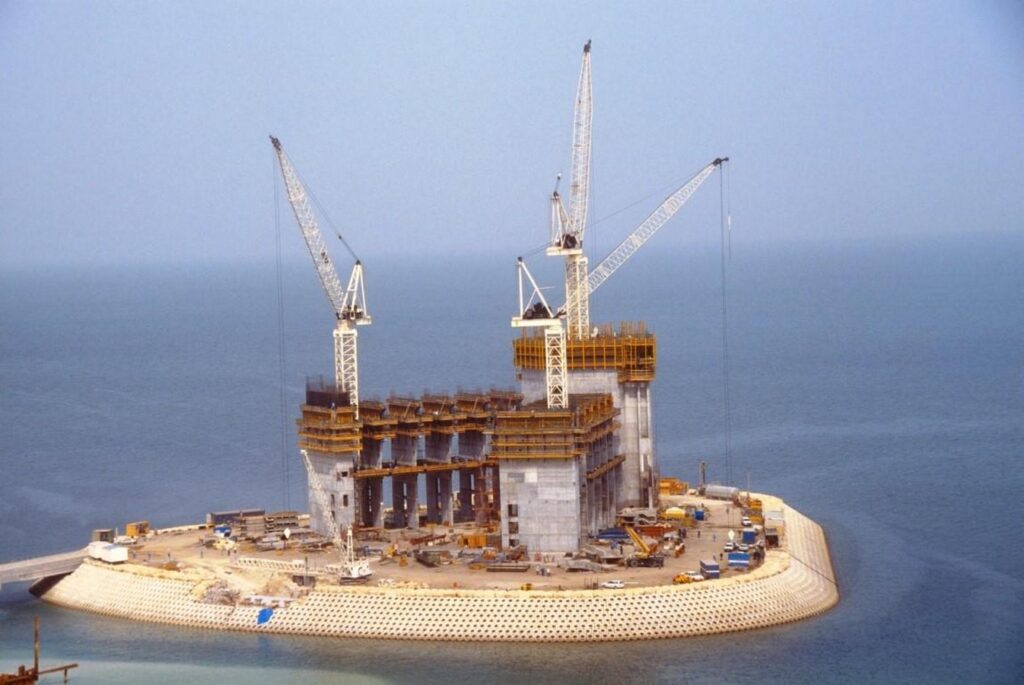

1. Residential Construction: Residential construction in Dubai focuses on meeting the housing needs of the city’s growing population. Key aspects of residential construction in Dubai include:
a. High-Rise Developments: Dubai is renowned for its high-rise residential towers and iconic skyscrapers. These projects offer luxury apartments, penthouses, and serviced residences, catering to both local and international buyers.
b. Master-Planned Communities: Dubai features master-planned communities that provide a holistic living experience, integrating residential, retail, recreational, and community facilities. These communities often include amenities such as parks, schools, healthcare centers, and leisure attractions.
c. Affordable Housing Initiatives: The government of Dubai has launched various initiatives to promote affordable housing, ensuring accessibility and affordability for residents across different income brackets. These initiatives aim to address the housing needs of the workforce and support sustainable urban development.
2. Commercial and Infrastructure Construction: Commercial and infrastructure construction projects in Dubai contribute to the city’s economic growth, business expansion, and urban infrastructure development. Key aspects of commercial and infrastructure construction in Dubai include:
a. Office Towers and Business Districts: Dubai’s business districts, such as Downtown Dubai, Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), and Dubai Media City, showcase state-of-the-art office towers and commercial developments. These projects provide modern workspaces and support the growth of various industries.
b. Retail and Entertainment Projects: Dubai’s construction market encompasses retail and entertainment developments, including shopping malls, leisure attractions, theme parks, and hospitality projects. The city is known for its world-class retail destinations and iconic leisure landmarks.
c. Transportation Infrastructure: Dubai’s construction sector has played a significant role in developing transportation infrastructure, including roads, bridges, airports, seaports, and metro systems. These infrastructure projects support seamless connectivity, facilitate trade, and enhance the city’s logistics capabilities.
3. Mega-Projects and Iconic Structures: Dubai is famous for its mega-projects and iconic structures that showcase architectural grandeur and engineering marvel. These projects have put Dubai on the global map and attract tourists and investors. Examples include the Burj Khalifa, Palm Jumeirah, Dubai Marina, and The World islands.
4. Sustainability and Innovation: Dubai’s construction market places increasing emphasis on sustainability and green building practices. The government promotes sustainable construction standards, energy-efficient designs, and environmentally friendly practices to reduce the carbon footprint and enhance the city’s sustainability.
5. Construction Regulations and Quality Standards: The construction market in Dubai operates within a robust regulatory framework overseen by entities such as the Dubai Municipality and the Dubai Development Authority. These entities enforce building codes, regulations, and quality standards to ensure safety, efficiency, and adherence to architectural guidelines.
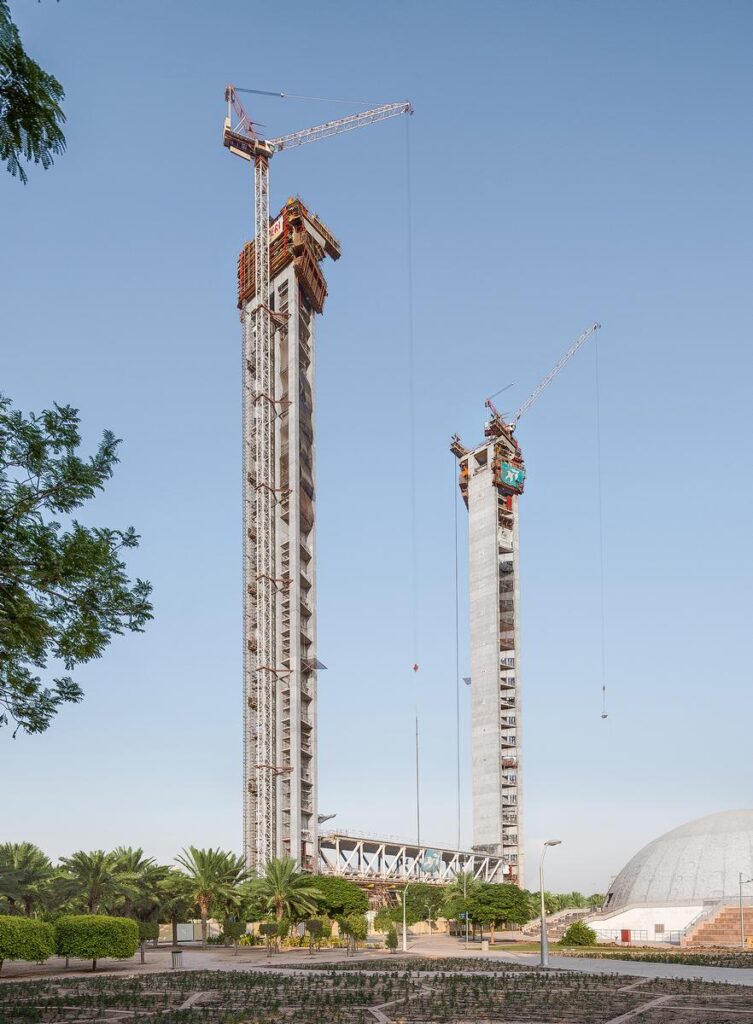

Dubai’s construction market continues to thrive, driven by the city’s vision for sustainable urban development, economic diversification, and commitment to creating a world-class built environment. The sector attracts global construction companies, architectural firms, and engineering professionals, contributing to Dubai’s status as a hub for innovation, design, and construction excellence.
Tourism
The tourism market in Dubai has been a significant driver of economic growth and has transformed the city into a global tourism hotspot. Dubai’s strategic location, modern infrastructure, diverse attractions, and luxury offerings have made it a preferred destination for leisure, business, and entertainment. Let’s explore the Dubai tourism market in more detail:
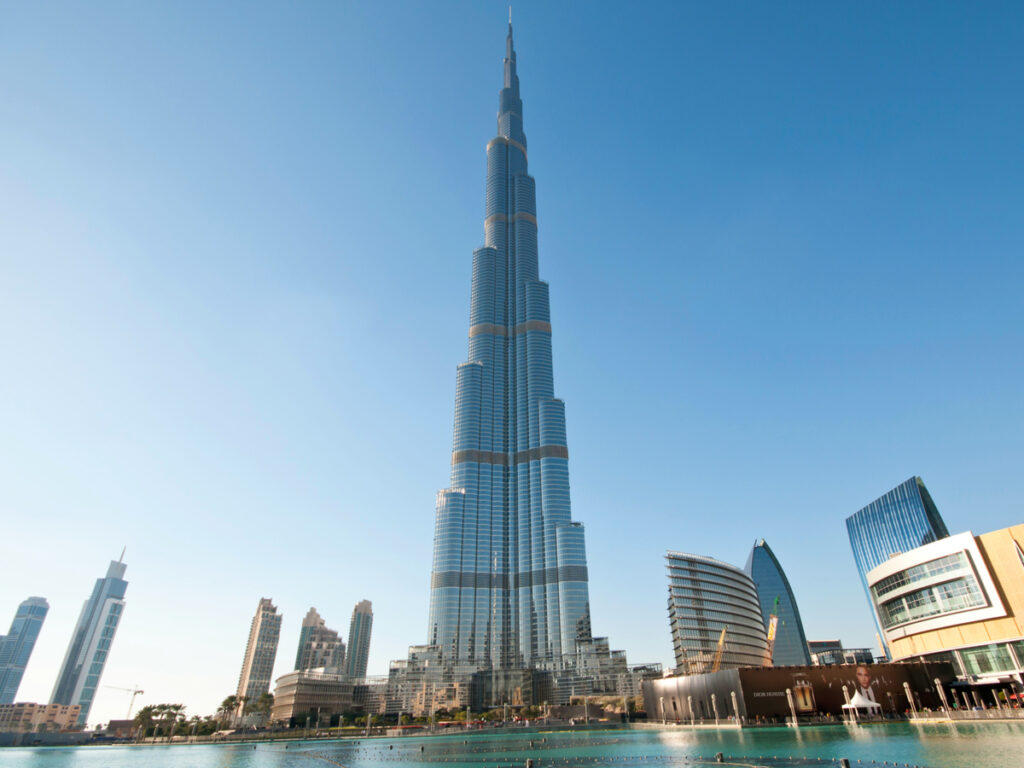

1. Tourism Infrastructure: Dubai’s tourism market is supported by extensive tourism infrastructure, including world-class airports, hotels, resorts, and entertainment facilities. Key aspects of the tourism infrastructure in Dubai include:
a. Dubai International Airport (DXB): Dubai International Airport is one of the busiest airports globally, serving as a major travel hub connecting various destinations. It provides excellent connectivity and facilitates the smooth arrival and departure of millions of tourists each year.
b. Hotels and Resorts: Dubai offers a wide range of hotels and resorts catering to different budgets and preferences. From luxury 7-star hotels to boutique accommodations, Dubai’s hospitality sector provides top-notch facilities and services to cater to the diverse needs of tourists.
c. Entertainment and Theme Parks: Dubai is known for its world-class entertainment and theme parks. Attractions like the Burj Khalifa, Dubai Mall, Atlantis The Palm, Dubai Parks and Resorts, and IMG Worlds of Adventure offer unparalleled entertainment experiences, attracting tourists from around the world.
2. Leisure and Entertainment Tourism: Dubai’s tourism market offers a plethora of leisure and entertainment opportunities, catering to various interests and demographics. Key aspects of leisure and entertainment tourism in Dubai include:
a. Shopping: Dubai is renowned as a shopping paradise, offering an array of luxury brands, international retailers, and traditional markets (souks). Malls like Mall of the Emirates and The Dubai Mall provide a unique shopping experience with a blend of retail, dining, and entertainment.
b. Beaches and Water Sports: Dubai’s pristine beaches, such as Jumeirah Beach and Kite Beach, attract sun-seekers and water sports enthusiasts. Visitors can indulge in activities like swimming, sunbathing, jet skiing, and parasailing.
c. Desert Safaris: Desert safaris are a popular tourist attraction in Dubai. Visitors can enjoy thrilling experiences like dune bashing, camel riding, quad biking, and traditional Arabian entertainment such as belly dancing and henna painting.
3. Business and MICE Tourism: Dubai has positioned itself as a major hub for business and MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions) tourism. Key aspects of business and MICE tourism in Dubai include:
a. Business Conventions and Events: Dubai hosts a wide range of international conferences, exhibitions, and business events. World-class venues such as the Dubai World Trade Centre and Dubai International Convention and Exhibition Centre attract business professionals from various industries.
b. Business Infrastructure: Dubai’s modern infrastructure, advanced telecommunications, and state-of-the-art business facilities make it an ideal destination for corporate meetings, conferences, and trade events. The city’s business-friendly environment and ease of doing business further enhance its appeal to the corporate sector.
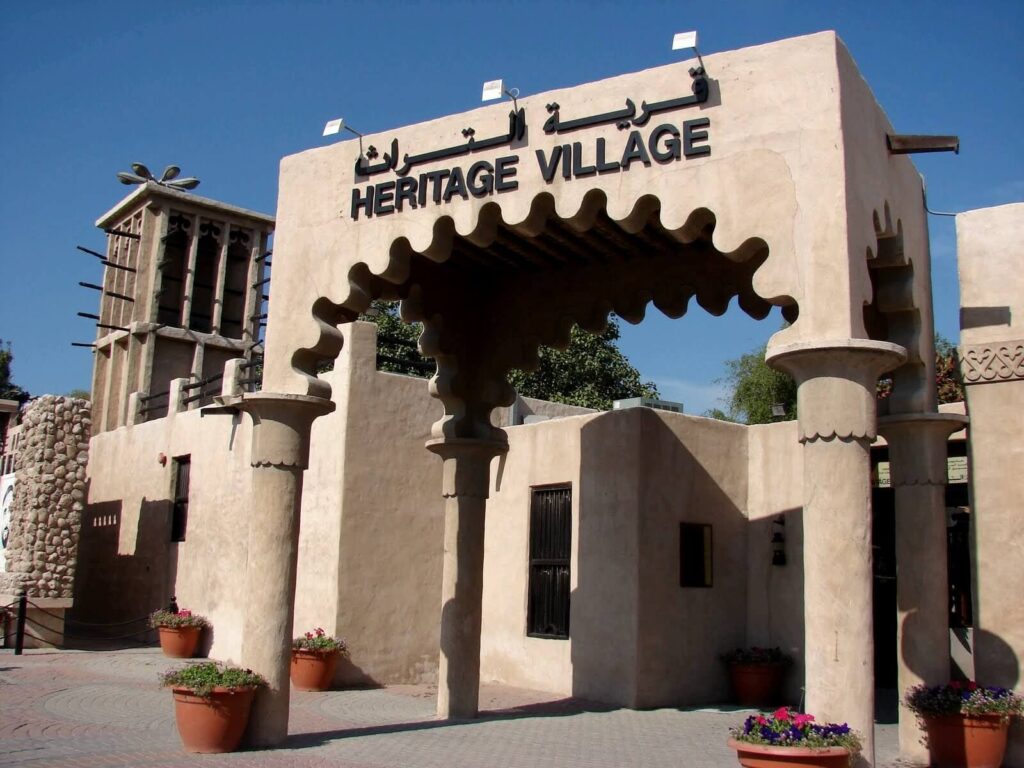

4. Cultural and Heritage Tourism: Dubai’s tourism market also highlights its rich cultural heritage and traditions. Key aspects of cultural and heritage tourism in Dubai include:
a. Historical Sites: Dubai features historical landmarks, such as Al Fahidi Historic District (Bastakiya), Dubai Museum, and Heritage Village, showcasing the city’s heritage and traditional architecture.
b. Cultural Festivals: Dubai hosts cultural festivals, such as Dubai Shopping Festival and Dubai Food Festival, which celebrate the city’s vibrant culture, art, music, and culinary traditions. These events attract visitors and offer unique cultural experiences.
5. Medical Tourism: Dubai has been growing as a medical tourism destination, offering advanced healthcare facilities and specialized medical treatments. Dubai Healthcare City and various internationally accredited hospitals attract patients seeking medical procedures, wellness retreats, and cosmetic treatments.
Dubai’s government, through entities like Dubai Tourism and Dubai Department of Tourism and Commerce Marketing (DTCM), promotes the tourism market, develops tourism strategies, and ensures the highest standards of visitor experiences. By continuously investing in infrastructure, enhancing offerings, and diversifying attractions, Dubai aims to strengthen its position as a leading global tourism destination.
Oil / Energy
The oil and energy market in Dubai has played a significant role in the city’s economic development and growth. While Dubai is known for its diversification efforts, the oil industry has historically been a crucial driver of the city’s economy. Let’s explore the oil and energy market in Dubai in more detail:
1. Oil Production and Reserves: Dubai has a modest oil production capacity compared to other oil-rich regions in the UAE. However, oil production has been a significant contributor to Dubai’s economy in the past. Key aspects of the oil market in Dubai include:

a. Reserves and Exploration: Dubai’s oil reserves are relatively small compared to other UAE emirates. The primary oil field in Dubai is the offshore Fateh field. The government continues to explore and evaluate potential oil and gas resources to maximize production and reserves.
b. Production and Export: Dubai’s oil production is managed by the Dubai Petroleum Establishment (DPE). Oil production has been declining in recent years as the government focuses on diversifying the economy. However, Dubai has historically exported oil to international markets, contributing to its revenue and economic growth.
2. Energy Diversification: Dubai has actively pursued diversification efforts to reduce its dependence on oil and transition to a more sustainable energy landscape. Key aspects of energy diversification in Dubai include:
a. Renewable Energy: Dubai has made significant strides in renewable energy development. The Dubai Clean Energy Strategy aims to generate 75% of Dubai’s total power from clean sources by 2050. The city has implemented large-scale solar projects, such as the Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park, which has become one of the world’s largest renewable energy projects.
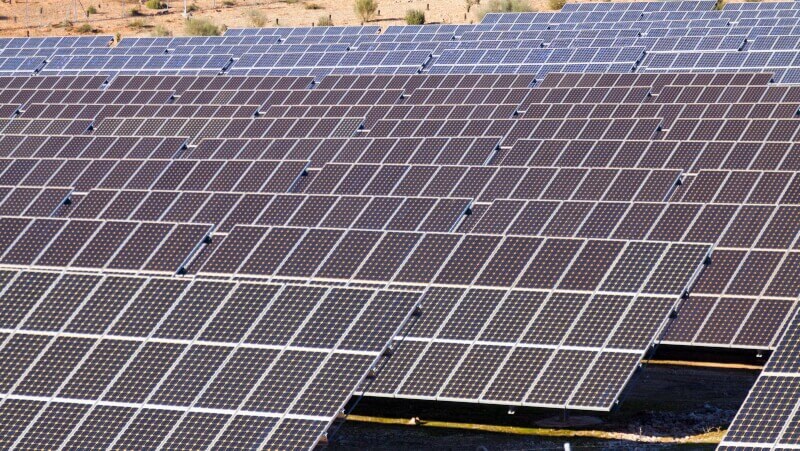

b. Nuclear Energy: Dubai has ventured into nuclear energy with the establishment of the Barakah Nuclear Power Plant. The plant, located outside of Dubai, aims to provide a sustainable and reliable source of energy to support the city’s growing electricity demand.
c. Energy Efficiency and Conservation: Dubai is committed to improving energy efficiency and promoting sustainable practices. Initiatives include energy-efficient building regulations, smart grid systems, and awareness campaigns to encourage energy conservation among businesses and residents.
3. Energy Infrastructure and Services: Dubai’s energy market extends beyond oil production and encompasses energy infrastructure, services, and utilities. Key aspects of the energy market infrastructure in Dubai include:
a. Electricity Generation and Distribution: Dubai’s electricity supply is managed by the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA). DEWA ensures a reliable supply of electricity to meet the growing energy demands of the city.
b. District Cooling: District cooling systems provide efficient cooling solutions for buildings and communities. Dubai has embraced district cooling technology, which reduces energy consumption and promotes sustainability in the cooling sector.
c. Gas Supply and Distribution: Natural gas plays a crucial role in Dubai’s energy market. Dubai’s gas supply and distribution infrastructure support various industries, including power generation, manufacturing, and residential usage.
Dubai’s government, through entities like the Dubai Supreme Council of Energy and DEWA, spearheads energy policies, regulations, and sustainability initiatives. By diversifying its energy mix, promoting renewable energy, and embracing sustainable practices, Dubai aims to establish itself as a global leader in clean energy and reduce its reliance on traditional fossil fuels.
Aviation
The aviation market in Dubai has flourished, establishing the city as a global aviation hub and a major player in the international air transportation industry. Dubai’s strategic location, state-of-the-art infrastructure, and business-friendly environment have attracted airlines from around the world, making it a key transit point and destination for both passenger and cargo traffic. Let’s explore the aviation market in Dubai in more detail:

1. Airports: Dubai is home to two major airports that handle a significant volume of air traffic:
a. Dubai International Airport (DXB): DXB is one of the busiest airports in the world in terms of international passenger traffic. It serves as a major hub for both full-service and low-cost airlines, connecting passengers to destinations worldwide. DXB offers state-of-the-art facilities, duty-free shopping, and a range of services to enhance the passenger experience.
b. Al Maktoum International Airport (DWC): DWC, also known as Dubai World Central, is Dubai’s second airport and primarily focuses on cargo operations. It has extensive cargo handling capabilities, serving as a vital logistics hub for international freight and facilitating global trade.
2. Major Airlines and Connectivity: Dubai’s aviation market hosts a wide range of international airlines, providing extensive connectivity to destinations worldwide. Key aspects of the aviation market in Dubai include:
a. Emirates Airline: Emirates, based in Dubai, is one of the world’s largest and most prestigious airlines. It operates an extensive network of passenger and cargo flights, connecting Dubai to major cities across all continents. Emirates has contributed significantly to the growth and global recognition of Dubai’s aviation market.
b. Flydubai: Flydubai, a low-cost carrier based in Dubai, offers affordable air travel to numerous destinations in the Middle East, Africa, Europe, and Asia. It complements Emirates’ network and serves as an important player in Dubai’s aviation market.
c. Code-Share Agreements: Dubai’s airlines have established numerous code-share agreements with international carriers, expanding their networks and enhancing connectivity. These agreements provide passengers with seamless travel options and the convenience of booking interline flights with multiple airlines.
3. Cargo and Logistics: Dubai’s aviation market is not limited to passenger travel, as it also excels in the cargo and logistics sector. Key aspects of cargo and logistics in Dubai’s aviation market include:
a. Freight Handling: Dubai’s airports, particularly DWC, serve as major hubs for air cargo operations. They provide extensive facilities, including cargo terminals, warehousing, and advanced logistics services, facilitating the movement of goods and supporting global trade.
b. Air Cargo Carriers: Dubai hosts several cargo airlines, including Emirates SkyCargo, which operates one of the largest freighter fleets globally. These cargo carriers offer dedicated cargo services, transporting various goods, including perishables, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and e-commerce shipments.
4. Airport Infrastructure and Services: Dubai’s aviation market boasts modern infrastructure and services that ensure a seamless travel experience. Key aspects of airport infrastructure and services in Dubai include:
a. Passenger Facilities: Dubai’s airports feature world-class passenger terminals equipped with extensive amenities, duty-free shopping, lounges, restaurants, and entertainment options. These facilities cater to the comfort and convenience of travelers.
b. Ground Handling and Support Services: Ground handling companies in Dubai provide a range of services, including baggage handling, aircraft servicing, fueling, and passenger assistance. These services ensure smooth operations and efficient turnaround times for airlines.
c. Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO): Dubai has established MRO facilities that offer maintenance and repair services for aircraft. These facilities provide technical expertise, spare parts, and maintenance solutions, supporting the aviation industry’s operational efficiency and safety.
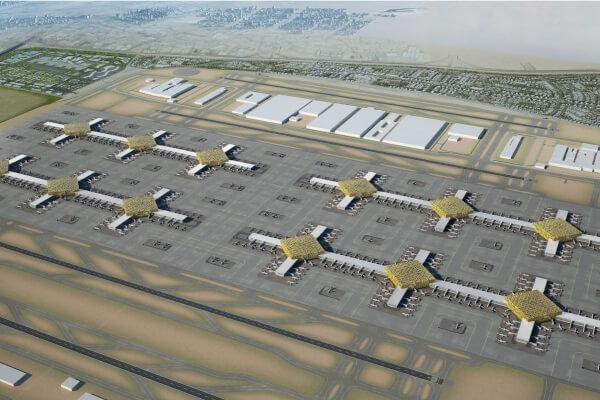

Dubai’s government, through entities such as the Dubai Civil Aviation Authority (DCAA) and Dubai Airports, ensures the regulation, oversight, and development of the aviation market. By continuously investing in airport infrastructure, attracting airlines, and fostering a business-friendly environment, Dubai aims to maintain its position as a global aviation hub and facilitate the growth of the aviation industry.
Legal Frameworks and Regulation
Dubai has a well-established legal framework and regulatory system that provides a stable and transparent business environment. The legal system in Dubai is influenced by both local laws and international best practices. Let’s explore the legal frameworks and regulations in Dubai in more detail:

1. Legal System: The legal system in Dubai is a dual system that combines elements of civil law and Sharia law. While civil law principles govern most commercial and civil matters, Sharia law influences personal and family law matters. Key aspects of the legal system in Dubai include:
a. Civil Law: Dubai’s civil law system is based on the legal framework established by federal laws in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). These laws govern various aspects of commercial transactions, contracts, employment, property, and intellectual property.
b. Sharia Law: Sharia law principles play a role in family law matters, including marriage, divorce, inheritance, and personal status. Sharia law is administered through the Sharia courts, which handle matters related to personal and family law.
2. Regulatory Authorities: Dubai has various regulatory authorities responsible for overseeing specific sectors and enforcing regulations. Key regulatory authorities in Dubai include:
a. Dubai Economy (Department of Economic Development): Dubai Economy regulates and supports economic activities in the Emirate. It sets guidelines and regulations for business licensing, commercial transactions, consumer protection, and competition.
b. Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA): DFSA is the independent financial regulatory authority governing the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). It ensures the integrity and stability of financial services provided within the DIFC, including banking, insurance, capital markets, and asset management.
c. Dubai Health Authority (DHA): DHA is responsible for regulating the healthcare sector in Dubai. It sets standards, licenses healthcare professionals and facilities, and oversees healthcare policies and initiatives.
d. Dubai Land Department (DLD): DLD regulates the real estate sector in Dubai. It manages property registration, oversees real estate transactions, and enforces regulations related to property ownership, leases, and development.
3. Company Formation and Commercial Law: Dubai provides a business-friendly environment with clear regulations and procedures for company formation and commercial activities. Key aspects of company formation and commercial law in Dubai include:
a. Free Zones: Dubai offers various free zones that provide incentives and benefits to companies operating within them. Free zones offer advantages such as 100% foreign ownership, tax exemptions, simplified licensing, and customs facilitation.
b. Commercial Companies Law: The UAE Commercial Companies Law governs company formation and operations. It provides guidelines for establishing different types of companies, such as limited liability companies (LLCs), joint-stock companies (JSCs), and branches of foreign companies.
c. Intellectual Property Protection: Dubai has regulations in place to protect intellectual property rights. The UAE’s Ministry of Economy is responsible for enforcing intellectual property laws and registering trademarks, patents, and copyrights.

4. Employment Law: Dubai has a comprehensive legal framework that governs employment relationships and protects the rights of both employers and employees. Key aspects of employment law in Dubai include:
a. Labour Law: The UAE Labour Law outlines the rights and obligations of employers and employees. It covers various aspects, including employment contracts, working hours, leave entitlements, termination procedures, and employee benefits.
b. Labour Market Regulation: Dubai has regulations to protect workers’ rights, ensure fair employment practices, and prevent any form of exploitation. This includes regulations related to minimum wages, health and safety standards, and anti-discrimination measures.
c. Free Zone Employment: Free zones in Dubai have their own employment regulations, which may differ from the general labour law. Free zone authorities oversee employment matters within their respective jurisdictions.
Dubai’s legal frameworks and regulations aim to provide a transparent and predictable business environment, protect the rights of individuals and businesses, and foster economic growth. These frameworks are regularly updated and refined to align with global best practices and meet the evolving needs of Dubai’s dynamic business landscape.
Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC)
The Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) is a prominent financial free zone in Dubai, established to facilitate the growth and development of the financial services sector. DIFC operates as an independent jurisdiction within Dubai, with its own legal and regulatory framework based on common law principles. It hosts a wide range of financial institutions, including banks, insurance companies, asset management firms, and capital market participants.

The DIFC provides a business-friendly environment, offering advantages such as 100% foreign ownership, tax exemptions, and state-of-the-art infrastructure. It has its own regulatory authority, the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), which ensures the compliance, transparency, and stability of financial activities within the DIFC. With its strategic location, robust legal system, and access to a pool of global talent, the DIFC has emerged as a leading financial hub in the region, attracting international businesses and contributing to Dubai’s position as a global financial center.
More information can be found in a separate post, Dubai International Financial Center.
Import/Export
Import and export activities play a crucial role in Dubai’s economy, contributing to its status as a global trading hub. The strategic location of Dubai, coupled with its world-class infrastructure, business-friendly environment, and efficient logistics services, has made it an ideal destination for importers and exporters. Let’s explore the import and export landscape in Dubai in more detail:

1. Trade Facilitation and Infrastructure: Dubai’s government has invested significantly in developing world-class infrastructure to facilitate import and export activities. Key aspects of trade facilitation and infrastructure in Dubai include:
a. Ports and Free Zones: Dubai boasts state-of-the-art ports, including Jebel Ali Port and Port Rashid, which are major gateways for goods entering and leaving the region. These ports offer modern container terminals, efficient cargo handling facilities, and customs clearance services. Free zones like Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA) and Dubai Airport Free Zone (DAFZA) provide specialized facilities and incentives to support import and export businesses.
b. Air Cargo Services: Dubai’s airports, especially Dubai International Airport and Al Maktoum International Airport, handle a significant volume of air cargo. The airports offer dedicated cargo facilities, customs clearance services, and efficient logistics support to expedite the movement of goods.
c. Customs Procedures: Dubai’s customs authorities, including the Dubai Customs, have implemented streamlined customs procedures to expedite the clearance of goods. Electronic documentation, automated processes, and risk-based inspections ensure efficiency and security in import and export operations.
2. Global Trade Connections: Dubai’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa has positioned it as a key trading hub connecting various markets. Key aspects of global trade connections in Dubai include:
a. Re-Export Trade: Dubai’s import-export market is characterized by a significant volume of re-export trade. Goods imported to Dubai are often re-exported to neighboring countries in the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia, leveraging Dubai’s efficient logistics network and trade links.
b. Global Supply Chains: Dubai’s import and export activities are integral to global supply chains, connecting manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers worldwide. Dubai’s efficient logistics services, availability of trade financing, and extensive network of shipping lines and airlines facilitate the seamless movement of goods across continents.
Dubai’s government, through entities like Dubai Exports and Dubai Chamber of Commerce and Industry, supports import and export activities by providing business facilitation services, market information, and trade promotion initiatives. The import and export sector in Dubai continues to thrive, contributing to economic growth, job creation, and reinforcing the city’s position as a global trading hub.
Free zones
Free zones in Dubai are designated areas that offer a business-friendly environment with various incentives and benefits for companies operating within them. These free zones are established to attract foreign investment, foster economic growth, and enhance Dubai’s position as a global business hub. Let’s explore the key aspects of free zones in Dubai:

1. Ownership and Tax Benefits: One of the main advantages of operating in a Dubai free zone is 100% foreign ownership. Companies established within free zones can be fully owned by foreign investors, eliminating the need for a local sponsor or partner. This ownership flexibility provides businesses with greater control over their operations and decision-making processes. Additionally, free zone companies enjoy tax benefits, including exemptions from corporate and personal income taxes, import and export duties, and capital gains taxes.
2. Simplified Company Setup: Setting up a company in a Dubai free zone is streamlined and efficient. The process is designed to be quick and hassle-free, with minimal bureaucratic hurdles. Free zones typically offer a one-stop-shop approach, providing services such as company registration, licensing, visa processing, and banking assistance all within the free zone itself. This simplified setup process allows businesses to start operations swiftly, saving time and effort.
3. Business Infrastructure: Dubai’s free zones provide modern and well-equipped infrastructure to support business activities. This includes state-of-the-art office spaces, warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and logistics centers. The infrastructure within free zones is designed to meet the specific needs of different industries, catering to various sectors such as technology, finance, logistics, healthcare, media, and more.
4. Sector-Specific Free Zones: Dubai’s free zones are often tailored to cater to specific industries or sectors, creating specialized business ecosystems. For instance, Dubai Internet City (DIC) focuses on information technology and digital media, Dubai Healthcare City (DHCC) specializes in the healthcare and medical sector, and Dubai Media City (DMC) is dedicated to the media and creative industries. These sector-specific free zones offer targeted support, networking opportunities, and a conducive environment for businesses operating within their respective sectors.
5. Supportive Services and Amenities: Dubai’s free zones offer a range of business support services and amenities to facilitate operations and enhance the overall business environment. These services may include access to professional business advisory services, legal and financial consultation, marketing and branding support, exhibition and conference facilities, networking events, and access to a pool of skilled professionals. Free zones also provide a range of amenities such as retail outlets, dining options, recreational facilities, and residential accommodations for employees.
6. Networking and Collaboration Opportunities: Being part of a Dubai free zone allows businesses to connect and collaborate with like-minded companies within the same industry. Free zones often organize networking events, industry-specific conferences, and exhibitions that provide opportunities for businesses to showcase their products and services, forge partnerships, and explore new business prospects. This collaborative environment fosters innovation, knowledge sharing, and business growth.
7. Regulatory Framework and Oversight: Each Dubai free zone operates under its own regulatory framework, administered by the relevant free zone authority. These authorities ensure compliance with the laws and regulations governing the specific free zone, including licensing requirements, company regulations, and industry-specific regulations. Free zone authorities also provide ongoing support, guidance, and oversight to companies operating within their jurisdiction.
A list of free zones provided in Dubai is shown below:
| Free Zone | Location | Specialty |
|---|---|---|
| Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA) | Jebel Ali | General Trading, Manufacturing, Logistics |
| Dubai Airport Free Zone (DAFZA) | Dubai International Airport | Aviation, Logistics, IT, Electronics |
| Dubai Silicon Oasis (DSO) | Dubai Silicon Oasis | Technology, IT, Research and Development |
| Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) | Downtown Dubai | Finance, Banking, Capital Markets |
| Dubai Knowledge Park (DKP) | Al Sufouh | Education, Training, Human Resource Management |
| Dubai Media City (DMC) | Dubai Media City | Media, Communication, Advertising |
| Dubai Internet City (DIC) | Dubai Internet City | Information Technology, Software Development |
| Dubai Healthcare City (DHCC) | Oud Metha | Healthcare, Medical Services |
| Dubai South Free Zone | Dubai South | Logistics, Aviation, Trade |
| Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC) | Jumeirah Lakes Towers | Commodities Trading, Gold and Diamond Trading |
Dubai’s free zones have been instrumental in attracting foreign investment, promoting economic diversification, and fostering innovation across various sectors. The benefits, incentives, and supportive ecosystem offered by Dubai’s free zones have made them a preferred choice for local and international companies looking to establish a presence in Dubai and leverage its strategic location and business advantages.
Video Tour
Conclusion
Dubai’s economy has evolved significantly over the years, transforming the city into a global business hub. The diversification efforts, focus on innovation and technology, and robust infrastructure have played a crucial role in its economic success.
With a favorable legal framework, thriving industries, and a commitment to sustainability, Dubai continues to attract investments and foster an environment conducive to business growth. The city’s future outlook remains optimistic, driven by its ability to adapt to changing global dynamics and embrace new opportunities.
FAQ
- What is the main source of revenue for Dubai’s economy?
- The main sources of revenue for Dubai’s economy include sectors such as real estate, tourism, finance, and trade. While oil played a significant role in the early stages of Dubai’s development, the city has successfully diversified its economy to reduce its reliance on oil revenue.
- How has Dubai diversified its economy?
- Dubai has implemented strategic plans to diversify its economy, focusing on sectors such as real estate, finance, tourism, and technology. The government has created a business-friendly environment, attracting foreign investments and promoting entrepreneurship.
- What are the major free trade zones in Dubai?
- Some of the major free trade zones in Dubai include Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA), Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC), Dubai Silicon Oasis (DSO), and Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). These zones offer various incentives and benefits for businesses, including tax exemptions and simplified procedures.
- How important is tourism for Dubai’s economy?
- Tourism plays a crucial role in Dubai’s economy, contributing significantly to its GDP. The city’s world-class attractions, luxury resorts, and vibrant entertainment options attract millions of tourists every year, generating revenue and creating employment opportunities.
- What is the role of Dubai Expo 2020?
- Dubai Expo 2020 is a global event that showcases innovation, technology, and culture. It provides a platform for countries to exhibit their achievements and attracts visitors from around the world. The expo is expected to boost tourism, stimulate economic growth, and create new business opportunities.
- How has Dubai become a global transportation hub?
- Dubai’s strategic location between Europe, Asia, and Africa has positioned it as a global transportation hub. The city has invested heavily in its airports, ports, and road networks, facilitating seamless trade flows and connecting markets worldwide.
- What is the significance of Islamic finance in Dubai?
- Dubai has emerged as a leading hub for Islamic finance, offering Sharia-compliant banking and financial products. Islamic finance plays a crucial role in attracting investments from Muslim-majority countries and promoting ethical financial practices.
- How is Dubai promoting sustainability and green initiatives?
- Dubai is committed to sustainability and has implemented various initiatives to reduce its carbon footprint and promote renewable energy sources. The city has invested in renewable energy projects and aims to become a global leaderin green finance and sustainable investments.
- What are the challenges faced by Dubai’s economy?
- Dubai’s economy faces challenges such as fluctuations in global oil prices, economic uncertainties in the region, and competition from neighboring cities and countries. Additionally, the city must continue to diversify its economy and adapt to changing global dynamics to maintain its position as a global business hub.
- What are the future prospects for Dubai’s economy?
- The future prospects for Dubai’s economy are promising. The city’s focus on economic diversification, innovation, and sustainability provides a strong foundation for growth. Strategic plans, such as the Dubai Industrial Strategy 2030 and Dubai Plan 2040, outline the city’s vision for sustainable economic development and its aspirations to become a knowledge-based economy.
Useful Links
- For more information about the Dubai economy check out the Department of Economic Development and Tourism.
- The main regulator for real estate investment is the Real Estate and Regulatory Authority, part of the Dubai Land Department.
- The Dubai Financial Center, which a major internal hub for investment and banking in Dubai.
- For a general guide about Dubai.
- Looking to visit Dubai? Check out the Dubai Entry Requirements for visitors.
- For a fantastic shipping experience check out the Dubai Mall.
- Check out the Burj Khalifa next door.
- Looking for fine dining options?
- There are many events during the year to promote business. One of these is the Dubai Shopping Festival.
- Looking to start a new business in Dubai? Check out the Dubai Startup scene.
- For Residence Visas in Dubai.
- Business Bay is a large commercial area within Dubai itself.
- For information on Dubai Free Zones.
- Checkout the DMCC at Jumeirah Lake Towers.
- Grocery shopping in Dubai is an important part of the economy. Check out our supermarkets in Dubai article.
- Moving you children to Dubai? Check out the Dubai Schools.
- Fancy a dune bashing trip with dinner afterwards?
Key Takeaways
- Dubai’s economy has transformed into a global business hub, attracting investors and professionals from around the world.
- The city’s GDP has shown consistent growth, with major contributions from sectors such as real estate, finance, tourism, and trade.
- Dubai’s legal framework and regulations are business-friendly, with free trade zones like DIFC offering unique benefits to businesses.
- The city’s strategic geographic location has made it a significant player in international trade, with well-developed infrastructure supporting seamless trade flows.
- The tourism and hospitality industry in Dubai is a major contributor to the economy, with iconic landmarks and world-class attractions attracting millions of tourists annually.
- Dubai’s commitment to infrastructure development has positioned it as a global transportation hub, with mega-projects and investments in transportation networks.
- The financial services sector, including Islamic finance, plays a vital role in Dubai’s economy, with the DIFC serving as a leading financial center in the region.
- Dubai’s focus on innovation and technology has led to the establishment of smart city initiatives and the promotion of startups and entrepreneurship.
- The city is committed to sustainability and has implemented initiatives to reduce its carbon footprint and promote renewable energy sources.
- Despite challenges, Dubai’s future outlook remains optimistic, driven by economic diversification plans and a vision for sustainable development.









